Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
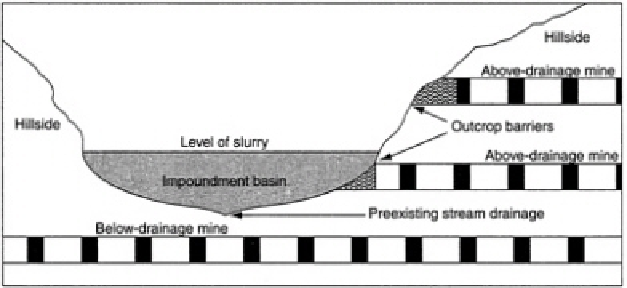
FIGURE 3.1 Cross section of schematic coal waste impoundment, depicting
underground mine workings above and below drainage with respect to the
impoundment; outcrop barriers are indicated.
For impoundments with both above- and below-drainage mine workings,
assessment of the strength and permeability of the material between the
impoundment and the underlying mines is important. This assessment includes
the distance and geologic conditions between the impoundment and the
underlying mines, the potential for hydraulic connection, and the potential for
collapse of the underground workings. At sites where above-drainage seams
have already been covered or inundated by slurry, this assessment is more
complex. Finally, for impoundments that will cross above-drainage coal seams
or workings in the future, it is essential to explore thoroughly the site along the
coal seam outcrop and to plug or seal off the contacts with the coal seam (see
Chapters
5
and
6
).
Proper engineering is critical at all stages of impoundment life: site
assessment, construction, operation, monitoring, and closure. The sections that
follow describe current approaches to each of these topics.
GENERAL IMPOUNDMENT SITING CRITERIA
Site investigations require a preliminary examination for site selection
followed by a detailed site study to develop safe and economical designs that
satisfy regulatory requirements. These investigations are primarily focused on
siting the embankment by assessing the factors influencing embankment
foundation strength, water seepage through the embankment foundation and


Search WWH ::

Custom Search