Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
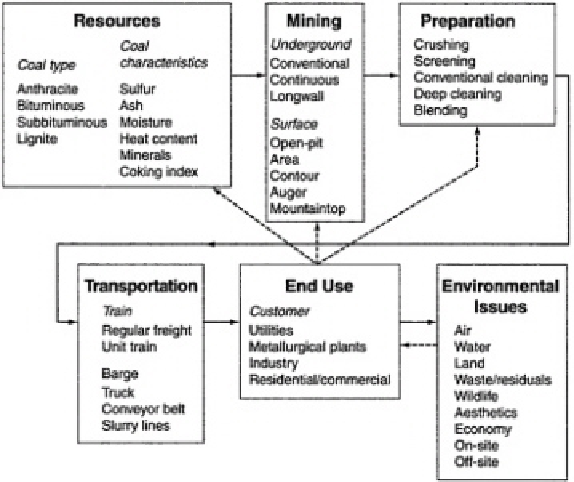
FIGURE 1.2 Coal system components. Dotted arrows indicate important
feedback to mining feasibility. Modified from Office of Technology
Assessment, 1979.
Limitations on sulfur dioxide (SO
2
) emissions from coal-fired power plants
have also contributed to the need for advanced coal-cleaning technology. Power
plants require coal of consistent quality (e.g., sulfur, ash, and heat content) to
comply with these regulations. In an effort to produce coals that allow power
plant operators to comply with standards established by the Clean Air Act,
various methods of removing pyrite (FeS
2
) from the coal have been developed.
In the past, much of this material would have entered the combustion chamber
with the coal and would have resulted in additional ash. Now, the pyrite is
removed, but it adds to the waste the preparation plant generates.
Finally, the quality of coal being mined in the Eastern United States has
declined as higher quality reserves have been depleted. Therefore, techniques
have been implemented to upgrade the coal product quality.
Previously, coal was cleaned by dry methods; however, a combination of
factors, such as particle size, dust, transport, health, safety, and noise, and the
better performance of wet processes have contributed to the near


Search WWH ::

Custom Search