Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Load
Load
178×102 UB 19
Profiled sheeting
D
=75
H
= 425
A142 Mesh reinforcement
B
=450
(a)
Elevation
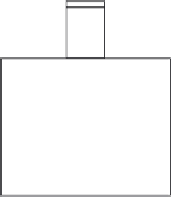
Figure 5.31 Arrangement of the pushout test conducted by Kim et al. [2.58, 2.59].
(b)
Side view
stud welded through deck in composite slabs with profiled steel sheeting.
The pushout test specimen arrangement is shown in
Figure 5.31
.Thesteel
beam used was a 178
102
19 kg/m UB section having two
13
65 mm headed studs welded on each flange of the steel beam through
the profiled steel sheeting. The profiled steel sheeting had a depth (
h
p
)of
40 mm, average width (
b
o
) of 136.5 mm, and plate thickness (
t
)of
0.68 mm. The composite concrete slab had a depth (
D
) of 75 mm, width
(
B
) of 450 mm, and height (
H
) of 425 mm. Reinforcement bar mesh of
6 mm diameter and 200 mm spacing between two bars was placed on the
top of the profiled sheeting. The concrete slabs of the pushout tests conducted
by Kim
et al.
[2.58, 2.59] had the average measured concrete cube strengths of
34.5 MPa, average tensile strength of 2.42 MPa, and Young's modulus of
21.7 GPa. The steel beam had the measured yield stress of 288 MPa and
Young's modulus of 189 GPa. The profiled steel sheeting had the measured
yield stress of 308 MPa and Young's modulus of 184 GPa. The headed shear
studs had the measured yield stress of 435 MPa. The load was applied on the
upper part of the steel beam. The movement of the composite concrete slabs
relative to the steel beamwas measured using six dial gauges attached to either
the profiled steel sheeting near the studs or the concrete top surface. The test-
ing arrangements and procedures as well as the specimen dimensions are
detailed in Kim
et al.
[2.58, 2.59]. On the other hand, pushout tests conducted
by Lloyd and Wright [2.57] provided the shear connection capacity of a
19
100 mm headed stud welded through deck in a composite slab with pro-
filed steel sheeting. The profiled steel sheeting had a depth of 50 mm, average










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search