Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
F
Ed
L
ð
maximum
¼F
D
:
L
:
g
g
+
F
L
:
L
:
g
q
F
Ed
L
ð
maximum
¼
3855
1
:
3 + 4465
1
:
35
¼
11,039
:
3 kN Tension force
ð
Þ
F
Ed
L
ð
minimum
¼
3855
1
:
3
158
:
9
1
:
35
¼
4797 kN Tension force
ð
Þ
It should be noted that, from the equilibrium of joint J
10
(see
4.6.3.3 Calculation of Force in the Lower Chord Member L
3
using the influence line method, we can follow the same procedures adopting
for member L
4
. Hence, the forces due to the dead and live loads can be
calculated as follows:
F
D
:
L
:
L
ðÞ¼
0
:
5
40
1
:
875
77
:
1
¼
2891
:
3kN
F
L
:
L
:
L
ð
positive
¼
450
1
ð
:
875 + 1
:
8
Þ
+0
:
5
40
1
:
875
45
:
65
¼
3365
:
6kN
F
L
:
L
:
L
ð
negative
¼
7
:
5
1
ð
:
875 + 1
:
8
Þ
0
:
5
40
1
:
875
2
:
45
¼
119
:
4kN
F
Ed
L
ð
maximum
¼F
D
:
L
:
g
g
+
F
L
:
L
:
g
q
s
a
4 m
B
J
8
A
L
2
L
3
s
10 m
30 m
g
vk
= 77.1 kN/m
450 kN450 kN
q
vk
= 45.65 kN/m
1.2 m
+
1.8
10 × 30/(40 × 4) = 1.875
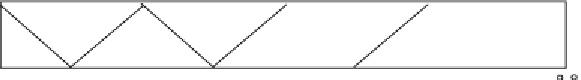
Figure 4.182 Determination of the tensile force in lower chord member L
3
using the
influence line method.


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search