Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The bearing is also subjected to a lateral force from the braking forces of
moving traffic as well as subjected to a longitudinal force from the reactions
of the lower wind bracings, which cause moments around longitudinal and
lateral directions of the bearing base, respectively. Similar to the roller bear-
ing, the material of construction for the bearings is cast iron steel (ISO 3755)
340-550 having a yield stress of 340 MPa and an ultimate stress of 550 MPa.
It should be noted that the overall height of the hinged bearing must be
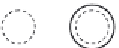
exactly the same as that of the roller bearing. The general layout and assumed
dimensions of the hinged line rocker bearing are shown in
Figure 4.125
.
The
braking
Q
lk
forces can be calculated as follows.
the forces). Also, the reactions from the lower wind bracings (
R
tot
) (see
Figure 4.124
for the direction of the forces) were previously calculated as
follows:
9kN
We can now determine the normal stress distribution due to the applied
loads, shown in
Figure 4.124
,
on the concrete foundation as follows:
R
tot
¼
212
:
M
y
I
y
x
N
A
M
x
I
x
y
f ¼
N
A
¼
2193
36
10
3
950
1100
¼
2
:
:
098MPa
9
10
3
M
x
I
x
y ¼
212
190
950
1100
3
:
550
¼
0
:
21MPa
=
12
6
10
3
M
y
I
y
x ¼
489
190
1100
950
3
:
475
¼
0
:
56MPa
=
12
f
max
¼
2
:
098
0
:
21
0
:
56
¼
2
:
87MPa
4
4
5
13.5
10
4
5.5
Figure 4.125 The designed roller and hinged line rocker fabricated steel bearings.








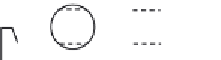




















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search