Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
shear force, even where cracking of concrete is assumed in global analysis.
The effects of cracking of concrete on the longitudinal shear force may be
taken into account, if in global analysis, and the effects of tension stiffening
and possible overstrength of concrete for the determination of the longitu-
dinal shear force. Where concentrated longitudinal shear forces occur, the
local effects of longitudinal slip should be taken into account. Otherwise,
the effects of longitudinal slip may be neglected. According to EC4, in
members with cross sections in class 1 or 2, if the total design bending
moment
M
Ed,max
¼M
a,Ed
+
M
c,Ed
exceeds the elastic bending resistance
M
el,Rd
, the nonlinear relationship between transverse shear and longitudinal
shear within the inelastic lengths of the member should be taken into
account. This applies in regions where the concrete slab is in compression,
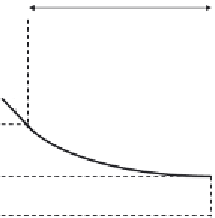
as shown in
Figure 3.27
.
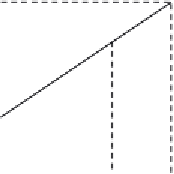
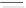
Shear connectors should be provided within the
inelastic length
L
A-B
to resist the longitudinal shear force
V
L,Ed
, resulting
from the difference between the normal forces
N
cd
and
N
c,el
in the concrete
slab at the cross sections B and A, respectively. If the maximum bending
moment
M
Ed,max
at section B is smaller than the plastic bending resistance
M
pl,Rd
, the normal force
N
cd
at section B may be determined using the sim-
plified linear relationship according to
Figure 3.32
.
N
c,d
N
c,el
M
el,Rd
M
Ed,max
V
L,Ed
B
A
L
A-B
M
X
M
pl,Rd
M
a,Ed
M
Ed,max
M
el,Rd
M
c,Ed
M
a,Ed
M
Ed,max
N
,
c
M
pl,Rd
N
c
f
N
c,d
N
cf
M
Figure 3.32 Determination of longitudinal shear in beams with inelastic behavior of


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search