Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
50
170
100
140
300
160
140
180
110
50
50
220
300
220
20
20
15
10
300
600
300
340
220
220
was derived, and the load-slip curves of the studs were plotted for the 12
push-off tests.
The behavior of shear connections in a composite beamwith a full-depth
were performed with variations of the stud shank diameter and the compres-
sive strength of the mortar.
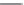
Figure 2.23
shows the push-off test specimen
used by the authors to evaluate the shear stud properties in a composite beam
with a full-depth precast slab. Different stud diameters (13, 16, 19, and
22 mm) were used with a stud height of 150 mm. The push-off tests were
and a bedding mortar layer 20 mm thick between the precast slab and the
steel beam. The load-slip curves of the stud were obtained, and the relation-
ship between the shear stud capacity and the stud diameters was plotted.
From the experimental work, the authors observed that the deformations
of the stud in a full-depth precast slab were greater than its deformations
in a cast in place slab. The static strengths of the shear connections agree































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search