Java Reference
In-Depth Information
24.4.3.6 Implementing
remove(index)
The
remove(index)
method finds the node at the specified index and then removes it. It can
be implemented as follows:
1
public
E remove(
int
index) {
2
if
(index <
0
|| index >= size)
return null
;
// Out of range
3
else if
(index ==
0
)
return
removeFirst();
// Remove first
4
else if
(index == size -
1
)
return
removeLast();
// Remove last
5
else
{
6 Node<E> previous = head;
7
8
for
(
int
i =
1
; i < index; i++) {
9 previous = previous.next;
10 }
11
12 Node<E> current = previous.next;
13 previous.next = current.next;
14 size--;
15
out of range
remove first
remove last
locate previous
locate current
remove from list
reduce size
return element
return
current.element;
16 }
17 }
Consider four cases:
1. If
index
is beyond the range of the list (i.e.,
index < 0 || index >= size
), return
null
(line 2).
2. If
index
is
0
, invoke
removeFirst()
to remove the first node (line 3).
3. If
index
is
size - 1
, invoke
removeLast()
to remove the last node (line 4).
4. Otherwise, locate the node at the specified
index
. Let
current
denote this node
and
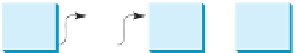
previous
denote the node before this node, as shown in Figure 24.17a. Assign
current.next
to
previous.next
to eliminate the current node, as shown in
Figure 24.17b.
head
previous current
current.next
tail
…
…
e
0
next
E
k
-1
next
e
k
next
e
k
-1
next
e
k
null
Delete this node
(a) Before the node is deleted.
previous
current.next
tail
head
…
…
e
0
next
e
k
-1
next
e
k
-1
next
e
k
null
(b) After the node is deleted.
F
IGURE
24.17
A node is deleted from the list.
Listing 24.6 gives the implementation of
MyLinkedList
. The implementation of
get(index)
,
indexOf(e)
,
lastIndexOf(e)
,
contains(e)
, and
set(index, e)
is omitted and
left as an exercise. The
iterator()
method defined in the
java.lang.Iterable
inter-
face is implemented to return an instance on
java.util.Iterator
(lines 126-128). The
LinkedListIterator
class implements
Iterator
with concrete methods for
hasNext
,
iterator




























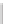




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search