Java Reference
In-Depth Information
create a thread for each connection. Here is how the server handles the establishment of a
connection:
while
(
true
) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// Connect to a client
Thread thread =
new
ThreadClass(socket);
thread.start();
}
The server socket can have many connections. Each iteration of the
while
loop creates a new
connection. Whenever a connection is established, a new thread is created to handle commu-
nication between the server and the new client, and this allows multiple connections to run at
the same time.
Listing 31.4 creates a server class that serves multiple clients simultaneously. For each con-
nection, the server starts a new thread. This thread continuously receives input (the radius of a
circle) from clients and sends the results (the area of the circle) back to them (see Figure 31.8).
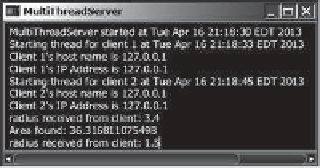
The client program is the same as in Listing 31.2. A sample run of the server with two clients
is shown in Figure 31.9.
Server
A server socket
on a port
A socket for a
client
A socket for a
client
. . .
Client 1
Client
n
F
IGURE
31.8
Multithreading enables a server to handle multiple independent clients.
F
IGURE
31.9
The server spawns a thread in order to serve a client.
L
ISTING
31.4
MultiThreadServer.java
1
import
java.io.*;
2
import
java.net.*;
3
import
java.util.Date;
4
import
javafx.application.Application;
5
import
javafx.application.Platform;
6
import
javafx.scene.Scene;
7
import
javafx.scene.control.ScrollPane;
8
import
javafx.scene.control.TextArea;
9
import
javafx.stage.Stage;
10


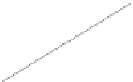

























Search WWH ::

Custom Search