Java Reference
In-Depth Information
96
finally
{
97
lock.unlock();
// Release the lock
release the lock
98
return
value;
99 }
100 }
101 }
102 }
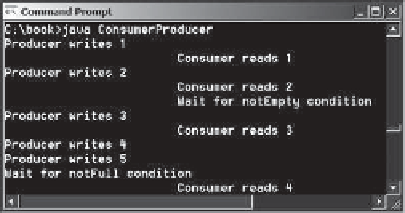
A sample run of the program is shown in Figure 30.19.
F
IGURE
30.19
Locks and conditions are used for communications between the Producer and
Consumer threads.
30.25
✓
✓
Can the
read
and
write
methods in the
Buffer
class be executed concurrently?
Check
30.26
When invoking the
read
method, what happens if the queue is empty?
Point
30.27
When invoking the
write
method, what happens if the queue is full?
Java Collections Framework provides
ArrayBlockingQueue
,
LinkedBlockingQueue
,
and
PriorityBlockingQueue
for supporting blocking queues.
Key
Point
Queues and priority queues are introduced in Section 20.9. A
blocking queue
causes a thread
to block when you try to add an element to a full queue or to remove an element from an
empty queue. The
BlockingQueue
interface extends
java.util.Queue
and provides the
synchronized
put
and
take
methods for adding an element to the tail of the queue and for
removing an element from the head of the queue, as shown in Figure 30.20.
blocking queue
«interface»
java.util.Collection<E>
«interface»
java.util.Queue<E>
«interface»
java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue<E>
+
put(element: E): void
Inserts an element to the tail of the queue.
Waits if the queue is full.
Retrieves and removes the head of this
queue. Waits if the queue is empty.
+
take(): E
F
IGURE
30.20
BlockingQueue
is a subinterface of
Queue
.




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search