Java Reference
In-Depth Information
✓
✓
3.1
List six relational operators.
Check
3.2
Point
Assuming that
x
is
1
, show the result of the following Boolean expressions:
(x >
0
)
(x <
0
)
(x !=
0
)
(x >=
0
)
(x !=
1
)
3.3
Can the following conversions involving casting be allowed? Write a test program to
verify your answer.
boolean
b =
true
;
i = (
int
)b;
int
i =
1
;
boolean
b = (
boolean
)i;
An
if
statement is a construct that enables a program to specify alternative paths of execution.
Key
Point
The preceding program displays a message such as “6
7 is false.” If you wish the
+
2
=
message to be “6
+
2
=
7 is incorrect,” you have to use a selection statement to make this
minor change.
Java has several types of selection statements: one-way
if
statements, two-way
if-else
statements, nested
if
statements, multi-way
if-else
statements,
switch
statements, and
conditional expressions.
A one-way
if
statement executes an action if and only if the condition is
true
. The syntax
for a one-way
if
statement is:
why
if
statement?
if
(boolean-expression) {
statement(s);
}
if
statement
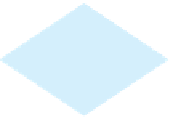
The flowchart in Figure 3.1a illustrates how Java executes the syntax of an
if
statement.
A
flowchart
is a diagram that describes an algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes
of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with arrows. Process operations are
represented in these boxes, and arrows connecting them represent the flow of control. A dia-
mond box denotes a Boolean condition and a rectangle box represents statements.
flowchart
false
false
boolean-
expression
(radius >= 0)
true
true
area = radius * radius * PI;
System.out.println("The area for the circle of" +
" radius " + radius + " is " + area);
Statement(s)
(a)
(b)
F
IGURE
3.1
An
if
statement executes statements if the
boolean-expression
evaluates to
true
.








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search