Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
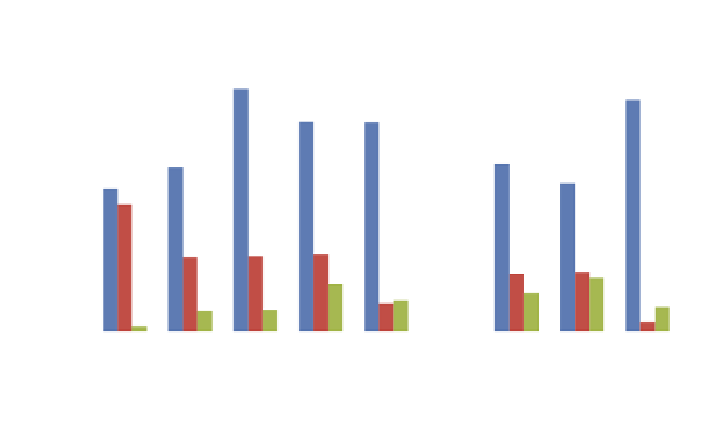
Soluble Protein
Total Lipids
Total Carbohydrates
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0
1
3
12
16
19
38
73
Age, days
Fig. 1. Biochemical composition changes during larvae and postlarvae development of
A.
purpuratus
. Arrow indicates metamorphosis.
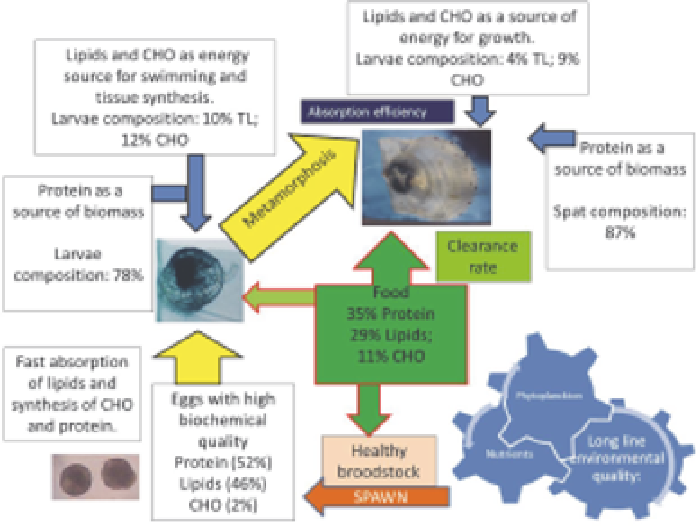
Fig. 2. Nutrient flows and biochemical pathways of planktonic larvae, spat and broodstock
of
A. purpuratus
under culture condition. High quality eggs from healthy broodstock favors
the use of lipids as a source of energy and synthesis of glycogen, while protein are used to
protein deposition . After metamorphosis, carbohydrates and lipids are used mainly as a
source of energy for maintenance and to accumulate protein via biomass production of spat.
Food quality, measured as protein content, and environmental quality (Temperature,
salinity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity etc.) determine the growth rate of bivalves, being the
clearance rate and energy absorption key of culture success.










Search WWH ::

Custom Search