Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
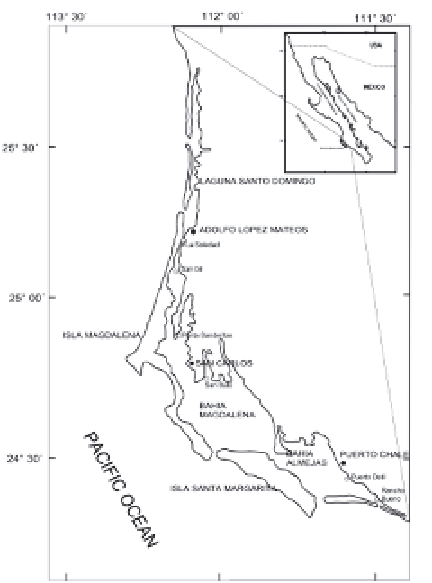
Fig. 1. Magdalena Bay location, Baja California Sur., México.
within Mexico. It is located between 24° 17´ and 25° 40´ N and 111° 30´ and 112° 15´ W. The
system is made of wide areas of wetlands especially in Laguna Santo Domingo and in
Almejas Bay.
Because of the physiography of the system it is regarded as a natural shelter for marine flora
and fauna, and for small fishing boats. This zone is influenced by the California Current and
by water that comes from the Equator, being a transition zone characterized by high
productivity (Parrish et al., 1981); the climate is warm and dry, classified as a semiarid
climate by Coppell system. The annual average temperature is of 20 °C, with a maximum of
41 °C in July-August, and a minimum of 4 °C in January-February. The mean total annual
average temperature is of 125 mm (Rueda-Fernández, 1983). In the warm season water
temperature column varies between 23 and 28 °C, while in the cold season it varies between
16 and 23.6 °C. Maximum salinity, ranging from 37.3 to 39.2 ups, is found in channels in the
lagoon system, while minimum salinity, from 34.0 to 34.5 ups, is registered in channels
connecting the system to the Pacific Ocean characterizing it as antiestuarine (Alvarez &
Chee, 1975; Acosta-Ruiz & Lara-Lara, 1978). Tides are semi-diurnal mixed. Maximum and
minimum dissolved oxygen level at the mouth of Magdalena Bay are of 6.85 and 3.68 mL/L
respectively; concentration of chlorophyll a fluctuates from 1.2 to 5.1 mg/m³; phosphates
vary from 3.09 to 0.62 µm, and water velocity from 0.24 to 1 m/s (Rueda-Fernández, 1983).
2. Magdalena Bay Mangrove
Mangroves often provide a source of wood products, providing subsistence for local
populations. However, logging is rarely the main cause of the loss of these trees. This is

Search WWH ::

Custom Search