Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
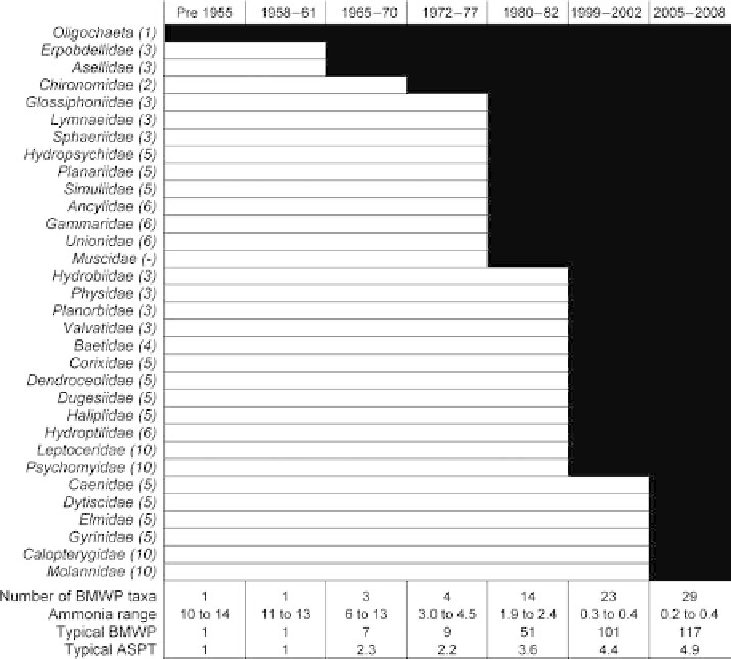
Figure 13.5.
Colonisation and succession of the River Tame at Chetwynd Bridge by
macroinvertebrate taxa. (Identification is to BMWP families/groups, see Wright et al.
2000
.) All taxa recorded over the relevant year are shown.
Oligochaeta, Chironomidae, Asellidae and Erpobdellidae were all, predictably,
recorded at ammonia concentrations around 5 10mg L
1
but taxon richness
was much lower by 2006 than at Chetwynd Bridge and no clean-water taxa
were present at concentrations below 2.5mg L
1
, though moderately tolerant
taxa such as Gammaridae, Ancylidae (limpets) and flatworms (e.g., Planariidae)
had recolonised. At Eagle Lane, moderately tolerant taxa such as Gammaridae
and Planariidae were present at the lower concentrations of ammonia
(1 2mg L
1
), but no clean-water taxa were recorded even to 2006. Thus, the
extent of succession differed at each site with the most improvement being
made at Chetwynd Bridge and the least at Eagle Lane, despite indications
of similar chemical improvements. The numbers of taxa observed per sample
compared with the numbers predicted by RIVPACS (Wright et al.
2000
) were
26/30 (2007) for Chetwynd Bridge, 18/32 (2005) for Lea Marston and 12/29