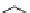Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Rate limiting step
N-yielding step
TrzN
or
AtzA
OH
OH
Cl
AtzB
N
N
N
N
N
N
H
2
O
HCl
H
2
O
NHC
2
H
5
H
7
C
3
HN
OH
H
7
C
3
HN
NHC
2
H
5
H
7
C
3
HN
N
NHC
2
H
5
N
N
Atrazine
Hydroxyatrazine
N
-isopropylammelide
Upper Pathway
H
2
O
N-yielding step
AtzC
NHC
3
H
7
OH
N-yielding step
N
N-yielding step
N
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
AtzF
O
AtzE
AtzD
2CO
2
+ 2NH
3
HO
OH
N
+
H
2
O
H
2
O
H
2
N
H + HCO
3
O
O
O
O
N
H
2
O
N
H
Cyanuric Acid
H
Allophanate
Biuret
Lower Pathway
Figure 10.3.
Complete atrazine degradation pathway found in Pseudomonas ADP and
several other gram-negative bacteria. Enzymatic reactions leading to nitrogen release
are indicated. The AtzA, AtzB and AtzC enzymes, hydrolyzing atrazine to cyanuric acid,
constitute the upper pathway, while the enzymes AtzDEF, hydrolysing cyanuric acid
to ammonia and carbon dioxide, comprise the lower pathway.
catabolism via TrzN, triazine hydrolase, an enzyme initially found in a Norcar-
diodes sp. strain (Mulbry et al.
2002
). TrzN has been now found in a variety
of gram-positive bacteria, including A. aurescens (Strong et al.
2002
), where it
has been purified to homogeneity (Shapir et al.
2006
). Like AtzA, the TrzN
hydrolytically displaces the chlorine from atrazine producing hydroxyatrazine.
These two enzymes, however, differ in substrate range. AtzA has narrow sub-
strate specificity and only functions to displace chlorine and fluorine leaving
groups, and transforms atrazine, simazine, desethylatrazine and terbutylazine
(de Souza et al.
1996
). In contrast, TrzN, a zinc amidohydrolase, displaces cyano,
azido, halide, S-alkyl and O-alkyl substituents (Shapir et al.
2005
), allowing
A. aurescens to metabolise a variety of s-triazine derivatives containing chlorine
plus N-ethyl, N-propyl, N-butyl, N-s-butyl, N-isobutyl or N-t-butyl substituents on
the s-triazine ring. This broad substrate range was shown to allow A. aurescens to
use 23 s-triazine substrates as the sole nitrogen source, including the herbicides
ametryn, atratone, cyanazine, prometryn and simazine (Strong et al.
2002
).
Moreover, atrazine substrate analogues containing fluorine, mercaptan and
cyano groups in place of the chlorine substituent could also be used as growth
substrates by this bacterium.
The lower atrazine degradation pathway in Pseudomonas ADP consists of three
enzymes, AtzDEF, resulting in ring cleavage and a subsequent transformation