Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8
winter (-9 °C to -5 °C)
summer (11°C to 15 °C)
6
4
2
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
distance [km]
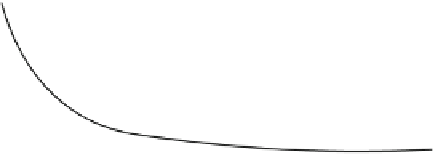
Fig. 8.2
Increased fuel consumption of a mid-size passenger car in cold weather
This temperature must be reached even with low environmental temperatures with
a cold engine.
At low temperatures, the fuel consumption of internal combustion engine
primarily increases with higher internal friction (see Fig.
8.2
)[
12
].
Several measures are useful for high thermal efficiency during ignition:
• Using a low engine speed with optimal compression;
• Minimizing leakage losses at the piston ring between the piston and the cylinder
wall;
• Decreasing
heat
losses
in
the
combustion
chamber
with
optimal
thermal
insulation;
• Applying high quality batteries to provide a high number of revolutions and high
power; and
• Using light running engine oil with low viscosity even at low temperatures.
8.3 Propulsion of Airplanes
The propulsion system of airplanes consists of the tanks, the fuel supply system,
the airframe, the nacelle and the engines. Predictions estimate a decrease in fuel
consumption by up to 25% with improved propulsion technology by the year 2050.
Significant improvements require:
• Improving the nacelle aerodynamics to reduce the load on the turbine and on the
compressor;
• Decreasing the size of the core engine;
• Increasing the thermal efficiency with higher turbine entry temperatures to
reduce air mass flow;



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search