Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
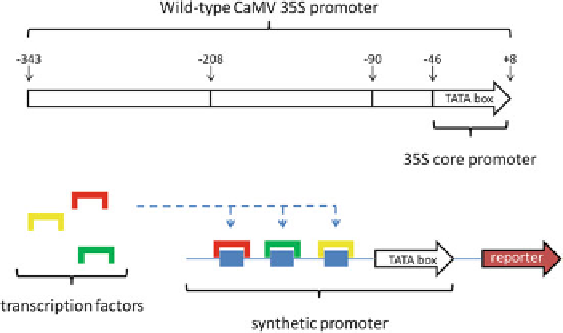
Fig. 10.4 Schematic representation of a synthetic promoter useful for bioindication purposes. The
core region of the CaMV 35S promoter is fused with a combinatorial engineering of cis-elements
(
blue boxes
) which, following the interaction with specific transcription factors, drives the reporter
expression under particular conditions
DNA fragment (
46 to +8 bp) of the CaMV 35S promoter as the main component
(Fig.
10.4
). The core-promoter region contains a TATA-box necessary for
recruiting RNA polymerase II and the orchestrated assembly of general transcrip-
tion factors to form the pre-initiation complex (Novina and Roy
1996
). The CaMV
35S core-promoter is ideal for transcription initiation and has been used in several
synthetic plant promoters in which combinatorial engineering of
cis
-element have
been introduced upstream of the core-promoter sequence.
The use of synthetic promoters allowing for targeted inducibility of a reporter
gene is of considerable interest to develop engineering strategies aimed at creating
plant bioindicators for real-time monitoring of nutritional status. For these purposes
promoter sequence domains or
cis
-elements conferring nutrient- and organ-
specificity should be combined in order to target the reporter expression in organs
(shoot and leaves) in which signals should be easily detectable.
Many different plant promoters have been described as able to restrict gene
expression to particular cells, tissues or organs. The
GaMYB2
promoter is cotton
fibre- and
Arabidopsis
trichome-specific, and can drive gene expression specifically in
glandular cells (head cells) of glandular trichomes in transgenic tobacco (Shangguan
et al.
2008
). Some
cis
-elements regulating tissue-specific gene expression have also
been identified. For instance, mesophyll expression module 1 (
Mem1
), a 41 bp
fragment of the
ppcA1
promoter, directs mesophyll-specific expression. The
tetranucleotide sequence, CACT has been identified as a key component of
Mem1
by evolutionary and functional studies (Gowik et al
2004
). More recently, Ye
et al. (
2012
) identified a rice green tissue-specific expression gene,
DX1
, and described
two novel tissue-specific
cis
-elements (GSE1 and GSE2) within the
DX1
promoter. In
particular, GSE1 acted as a positive regulator in all green tissues, whereas GSE2 acted
as a positive regulator only in sheath and stem tissues.