Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
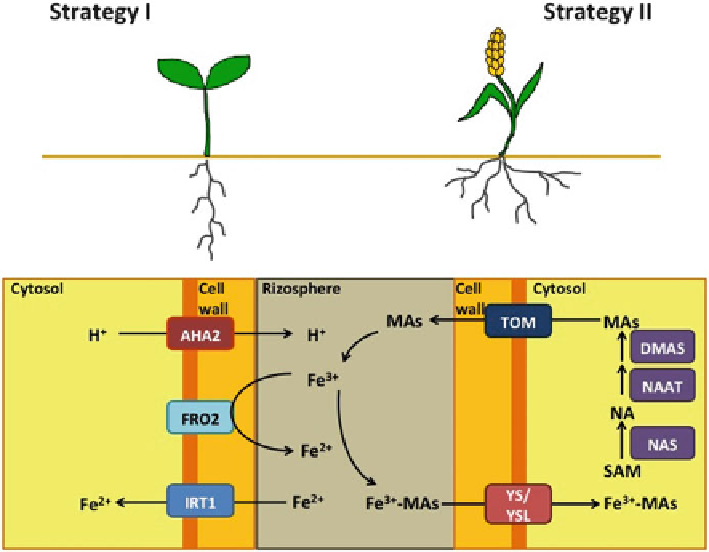
Fig. 5.1 Fe deficiency responses in plants. Strategy I (non-graminaceous plants) and Strategy II
(graminaceous plants) are presented. In the
rectangles
the key enzymes of the two strategies are
shown. Abbreviations:
AHA2 Arabidopsis
H
+
-ATPase,
DMAS
deoxymugineic acid synthase,
FRO2
ferric chelate reductase 2,
IRT1
iron regulated transporter 1,
MAs
mugineic acids,
NAAT
nicotianamine aminotransferase,
NAS
nicotianamine synthase,
TOM
transporter of mugineic acids,
YS
yellow stripe,
YSL
yellow stripe like. YSL refers to orthologs of YS in plants other than maize
different steps of the strategy I have been identified and cloned and Fe deficiency
results in an up-regulation of their expression. Firstly, the H
+
-ATPase family
(HA) excretes protons into the rhizosphere to increase Fe solubility (Palmgren
2001
). In
Arabidopsis
the
HA2
gene particularly is induced in Fe deficiency
(Santi and Schmidt
2009
). The reduction of Fe
3+
is catalysed by the ferric-chelate
reductase oxidase 2 (FRO2) in
Arabidopsis
(Robinson et al.
1999
) and by FRO1 in
pea (Waters et al.
2002
). FRO proteins are integral membrane proteins that belong
to a superfamily of flavocytochromes and can transfer electrons from cytosolic
NADPH to FAD across the plasma membrane (Robinson et al.
1999
).
FRO2
was
isolated as allelic to the
frd1
mutants in
Arabidopsis
(Yi and Guerinot
1996
). These
mutants are not able to induce the Fe chelate reductase activity, although they are
still able to acidify the rhizosphere upon Fe deficiency. Moreover, these mutants
cannot translocate radiolabeled Fe from root to the shoot when Fe is provided as
chelated Fe
3+
. Altogether these results shown that FRO activity is uncoupled from
the HA activity and that Fe
3+
reduction to Fe
2+
is a prerequisite for the transport.