Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
-1
1972
1973
1974
1975
1976
1977
1978
1979
1980
1981
1982
Year
Fig. 18.18
Potential precipitation surplus during years 1972-1982
calculations showed that removing only water from aqueous solutions results in a
pH decrease (for a similar geochemical system, i.e., only cation exchange and equi-
librium with gibbsite). Another factor intensifying the pH decrease was the greater
mobility of anions (Cl
−
and Br
−
) compared to cations. Thus, the physical factors
of having a decreasing water content and upward flow of water and contaminants
caused the pH to decrease when
P
E
p
is negative. It should be noted that the
p
H
in reality is also affected by other geochemical or biological processes not included
in the invoked conceptual model. For example, soil carbon dioxide concentrations
that usually change in response to biological activity and moisture status of the soil
can also affect soil
p
H(Šimunek and Suarez
1993
).
Although upward flow during the summer had almost no effect on the total
amount of heavy metals in the surface horizon due to the low mobility of these
elements, the aqueous concentrations of the metals did vary significantly during
the season. Several factors contributed to this. First, because of lower water con-
tents, the concentration of all aqueous species increased during summer periods.
Changes in aqueous concentrations in turn caused changes in the cation exchange
equilibrium, thereby promoting monovalent cations to sorb onto the cation exchange
complex and bivalent cations to desorb into solution. This explains also the dif-
ference between
T
Na,aq
and
T
Ca,aq
during the summer near the soil surface. The
aqueous concentration of Na was controlled more by the cation exchange complex
than that of Ca due to preferred adsorption of Na during dry soil conditions. This
process is further amplified by the increased supply of monovalent cations due to
upward flow of water during summer, leading to relatively more sorption of the
monovalent cations and higher concentrations of divalent cations and heavy metals
in the liquid phase. The complexation of cadmium with Cl contributed also to the
−



















































































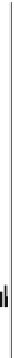

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search