Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10000
10000
α
= 0.1
1000
1000
n = 1.25
100
100
1
10
10
2
10
1
1
5
0.1
0.1
0.01
0.01
0
0.2
1
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0.4
0.6
0.8
Saturation degree Se
Saturation degree Se
α
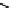
Fig. 18.5
Dependency of soil water characteristic curves on Van Genuchten parameters
(keeping
n
fixed at 1.25) (
left
)and
n
(keeping
α
fixed at 1) (
right
). Saturation degree
S
e
is used rather than
water content
While some definitions of
θ
r
have been proposed (e.g., the water content where
the hydraulic conductivity becomes first zero during drying),
θ
r
in practice is best
treated as a fitting parameter without any physical significance
.
Another parametric description of the moisture retention characteristic is the
equation of Brooks and Corey (
1964
):
θ
s
−
θ
r
)
h
n
h
e
θ
r
+
(
h
<
h
e
θ
(
h
)
=
(18.4)
θ
s
h
≥
h
e
where
h
e
is the air-entry value [L] and
n
is the pore-size distribution index that
characterizes the width of the pore-size distribution (or the steepness of the retention
function). Like
n
in Eq. (
18.3
), the value of
is relatively large for soils with a
relatively uniform pore-size distribution, but small for soils having a wide range of
pore sizes.
A large number of experimental techniques can be used to measure the water
retention curves. These techniques include methods using a hanging water column,
pressure cells, pressure plate extractors, suction tables, soil freezing, and many other
approaches (Dane and Hopmans
2002
). Alternatively, soil hydraulic parameters may
be obtained with pedotransfer functions using information on textural class or textu-
ral fractions (and some additional information). Pedotransfer functions are statistical
relationships that use easily available soil data to estimate the soil hydraulic param-
eters (Bouma
1989
;Leijetal.
2002
; Pachepsky and Rawls 2004; Pachepsky et al.
2006
).
λ
18.2.1.2 Hydraulic Conductivity
Another important soil hydraulic property is the
unsaturated hydraulic conductivity
function
.The
hydraulic conductivity
characterizes the ability of a soil to transmit
water, and as such is inversely related to the resistance to water flow. The hydraulic







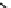






























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search