Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
('good' or 'bad'; acceptable or unacceptable, when the Risk Index is lower or higher
than 1.0, respectively) the Risk Index allows for classification of risk qualifications,
although this is a subjective process, into classes such as, for example, a 'very high
human health risk', when the Risk Index exceeds a value of 10. Moreover, a Risk
Index offers possibilities for the scaling of human health risks, which is useful in
terms of priority setting. It should be noted, however, that in regard to classification
and ranking of risks, the Risk Index assumes a linear relationship with seriousness
of human health effects, whereas dose-response curves generally are not linear. Thus
a Risk Index of 10 is generally not 10 times worse than a Risk Index of 1.
5.5.2 Soil Quality Standards
Generally, Soil Quality Standards are derived for generic Risk Assessment purposes,
that is, for Risk Assessments not related to a specific site. For the derivation of
Soil Quality Standards, the Estimated Exposure relates to the
potential
exposure.
Potential exposure is defined as the exposure that would occur under specific, stan-
dardized conditions in terms of geographical conditions (e.g., relating to soil type,
soil properties, depth of groundwater table) and human behaviour (also exposure
characteristics: e.g., relating to residence time, amount of home-grown vegetable
consumption). To be able to calculate the potential exposure, a generic
expo-
sure scenario
must be constructed, in which the above-mentioned conditions and
characteristics are described and quantified.
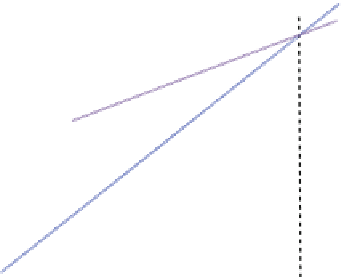
In regard to the derivation of Soil Quality Standards, the Risk Characterisation
is best explained graphically (see Fig.
5.5
). In this graph the relevant
potential total
RfD
Total soil concentration (mg.kg
-1
dw
)
C
soil
solubility
human health-based SQS
Fig. 5.5
Average life-long human exposure (
potential exposure
) as a function of total soil concen-
tration; the critical exposure (reference dose; RfD); the resulting human health-based soil quality
standard (human health-based SQS);
C
soil
solubility
=
concentration in soil at which the water
solubility is reached









Search WWH ::

Custom Search