Database Reference
In-Depth Information
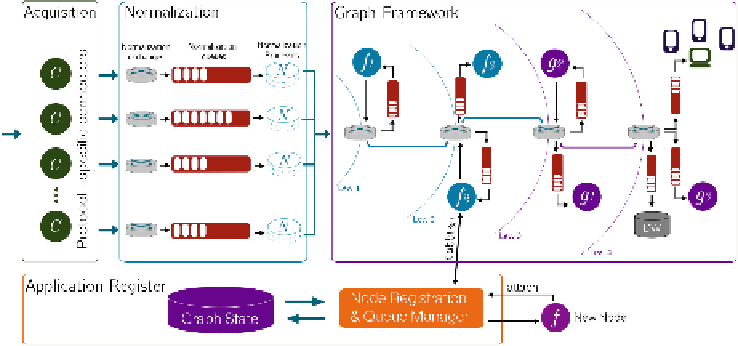
Fig. 4.
The complete Graph Cloud Architecture with reference to the data stream flow
between all building blocks, from IoT data sources to final consumers.
2.1 Acquisition Module
The
Acquisition Module
represents the entry point for external IoT networks
of smart objects to the Cloud architecture. Its purpose is to collect raw data
from different and heterogeneous data sources and make them available to the
other functional blocks. It is important to underline that several application-layer
protocols can be implemented by smart objects. For this reason, the Acquisition
Module includes a set of different connectors in order to properly handle each
protocol-specific incoming data stream.
2.2 Normalization Module
Raw data are generally application-dependent, thus a
Normalization Module
has
been designed in order to normalize all the collected information and generate a
representation suitable for processing. The normalization procedure is made by
fundamental and atomic operation on data such as: (i) the suppression of useless
information (e.g., unnecessary headers or meta-data); (ii) the annotation with
additional information; and (iii) the translation of the payload to a suitable
format. In order to handle the huge amount of incoming data eciently, the
normalization step is organized with protocol-specific queues and
Exchanges
.
An
Exchange
works as a router in the system and dispatches incoming data to
one or more output queues depending on dynamic routing rules. As shown in
the normalization section of Fig.
4
, the information flow originating from the
Acquisition Module is handled as follows:
- all data streams relative to a specific protocol are routed to a dedicated protocol-
specific exchange, which forwards them to a protocol-dedicated queue;
Search WWH ::

Custom Search