Database Reference
In-Depth Information
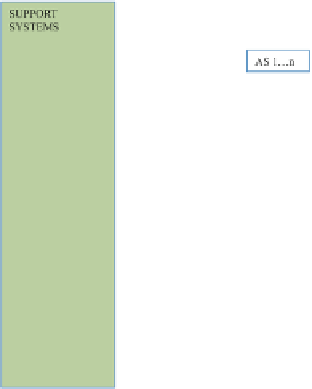
Fig. 2.
IMS layered architecture with main interfaces
different transmission technologies and inter-working between different media
formats [
5
]. The supporting functions encompasses functions for: operation and
management, network and self-provisioning, Domain Name System/Telephone
Number Mapping functionality, etc. A brief description of main functionalities
used in our use case that are included in IMS is given below.
The Call Session Control Function (CSCF) is an essential node in IMS for
processing signaling, using SIP as the signaling protocol [
3
]. It also provides
support for Internet protocols. The CSCF handles session establishment, modi-
fication and release of IP multimedia sessions using the SIP/SDP protocol suite.
The CSCF can act as Proxy CSCF (P-CSCF), Serving CSCF (S-CSCF) or Inter-
rogating CSCF (I-CSCF).
I-CSCF is the contact point inside an operator's network for all SIP requests
destined to a user of that network operator. It locates the S-CSCF that was
assigned to the user at registration through interaction with HSS.
S-CSCF performs session control services for the endpoint. This includes
routing of originating requests to the terminating network and routing of ter-
minating requests to the P-CSCF. The S-CSCF supports establishment, modifi-
cation and release of IP multimedia sessions using the SIP/SDP protocol suite.
The S-CSCF also decides whether an application server is required to receive
information related to an incoming SIP request outside a dialog to ensure appro-
priate service handling. The decision at the S-CSCF is based on trigger informa-
tion received from the HSS, as an initial filter criteria. The trigger information
includes identifiers of the application server(s). The trigger information can then
provide indirect service invocation through an ISC interface towards the Appli-
cations layer.






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search