Database Reference
In-Depth Information
5.1 Autonomic IoT Data Collection
LSM-Light module plays the role of central component of OpenIoT platform [
16
] and
an instance was used in Super Stream Collider. It is used to collect data from different
sensor sources, annotate and transform data into linked data. In SSC-Fed4FIRE
experiments, an LSM-Light client module was distributed in a cluster of 10 nodes. The
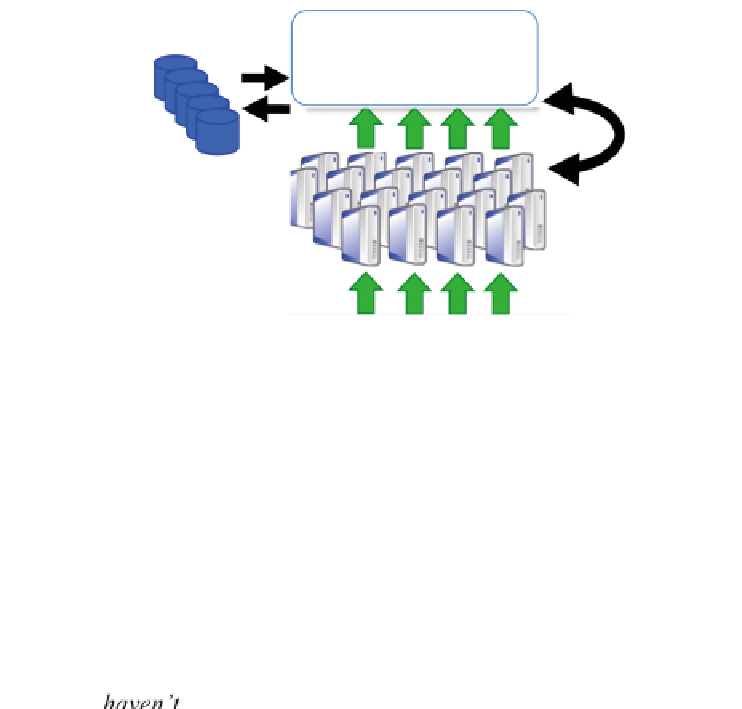
architecture of the deployment is shown in Fig.
5
.
Linked data
storage
LSM-Light Server
LSM-
Light
clients
Smart Santander Sensor Data
Fig. 5. LSM-Light architecture for SSC-Fed4FIRE experiment.
In SSC-Fed4FIRE experiment, a Hadoop cluster for fetching IoT data was used.
Fetching tasks for over 2,000 Smart Santander sensor data sources including: humidity,
air quality, noise pollution, parking status, temperature information was scheduled. The
main reason of using Hadoop is to enable the autonomic feature by minimizing the
fetching cycles, which cannot be processed manually or in a single machine.
The majority of the data sources in the deployment are published through HTTP as
Web services or RESTful APIs, which are pull-based mechanisms. For these sources,
the LSM-Light clients periodically fetch each data source to collect raw sensor data and
transform it into triples. The fetching operations are built as asynchronous tasks,
scheduled in the fetching cluster. The fetching algorithm can be described as follow:
if sensor be registered in the system
Register sensor
while true
do
Collect raw data from sensor
Transform raw sensor data into RDF
Send RDF data to LSM-Light server
Set system sleep for specific scheduled time


Search WWH ::

Custom Search