Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Chroma vs. TMA (cyan)
70
60
50
g
=0
g
=30
g
=50
g
=100
40
30
20
10
0
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
TMA (mg/cm
2
)
FIGURE 10.34
Effect of gloss on Chroma, C* (for different values of TMA).
where
x is the vector of the inputs to the system
y is the one of the outputs
It is interesting to observe the nice symmetry coming out of the models since the
entire system, which can be viewed as a complete deterministic characterization of a
dot printer, consists of a cascading of the process models (where the output of a
model becomes an input to the next one), the fusing and the color model. Therefore,
we can get the re
ectance curve or tristimulus values as functions of the actuators, as
illustrated in block diagram form in Figure 10.36.
L
* vs. TMA (cyan)
120
g
=0
g
=30
g
=50
g
= 100
100
80
60
40
20
0
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
TMA (mg/cm
2
)
(a)
FIGURE 10.35
(a) Effect of gloss on lightness, L* (for different values of TMA) and
(continued )




































































































































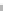
































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search