Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
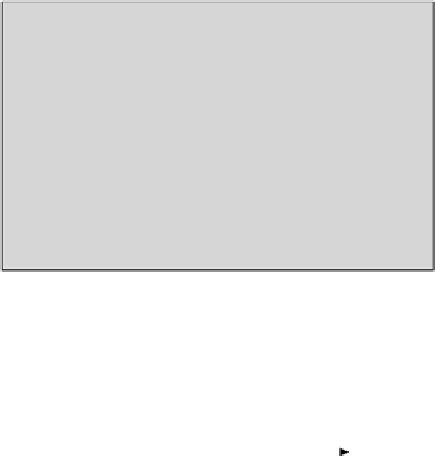
Raster data
Scanner
Digital camera
…
Workstation
Document
generation
Image processing
Color management
Printer
drive
C
Digital front end
(DFE)
Postscript
M
Image processing
Enhancement
Noise removal
Segmentation
Y
Color management
Calibration
Color rendition
dictionary (CRD)
K
FIGURE 1.2
High level steps in the prepress area and DFE for digital printing.
a raster format (JPEG, TIF, etc.)
can be integrated into documents using a
variety of desktop publishing software packages such as Microsoft Of
—
ce (Word,
PowerPoint, etc.), Quark XPress, Freehand, and so on. De
ning spot
=
process colors,
checking for fonts, setting the right screens (halftone dots), inserting
editing multiple
pages are done in the prepress area. Supported stocks are entered to meet the customer
order. Trapping is done to the documents to compensate for the small amount of
misregistration in the printing system. Without trapping, unnecessary white gaps may
appear between two colors that are supposed to be touching.
The assembled job is then sent for proo
=
ng without actually printing it on the
press. The proo
ng is sometimes done on another digital printer and often on a well-
calibrated monitor. If problem pages are found within the proo
ng stage, the job is
further checked to handle corrections in the prepress area. Most documents contain a
mixture of vector and raster type data. Vector data includes line drawings, arrows,
boxes, line art, etc., as created by applications like Microsoft Word. Raster data, on the
other hand, are usually generated by a scanner or digital camera (still or video). Once
the documents have been designed on the desktop, they are assembled into jobs,





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search