Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
||Ax||
y
2
x
2
y=Ax
x
1
y
1
x
1
y
1
x =
y =
x
2
y
2
||x|| =
1
FIGURE 3.17
Matrix norm.
Matrix norm is a measure of boundness of that matrix. The concept of matrix norm
for a 2
2 matrix is illustrated in Figure 3.17.
The matrix norm depends on vector norm, for example, if the vector norm is l
1
norm then the matrix norm is based on vector l
1
norm. We consider three cases
corresponding to p
¼
1, p
¼
2, and p
¼1
.
Case I:
p
¼
1
In this case, the matrix norm becomes
X
m
k
A
k
1
¼ max
k
x
k
1
¼
1
k
Ax
k
1
¼ max
a
ij
(
3
:
143
)
j
i
¼
1
Therefore,
k
A
k
1
is equal to the longest column sum, which means that to
nd the
p
¼
1 norm, compute the sum of absolute values of each column and pick the
maximum.
Case II:
p
¼1
In this case, the matrix norm becomes
X
m
k
A
k
1
¼ max
k
x
k
1
¼
1
k
Ax
k
1
¼ max
1
j
a
ij
j
(
3
:
144
)
i
j
¼
Therefore,
k
A
k
1
is equal to the longest row sum, which means that to
nd the
p
¼1
norm, compute the sum of absolute values of each row and pick the
maximum.
Case III:
p
¼
2
In this case, the matrix norm becomes
k
A
k
2
¼ max
k
x
k
2
¼
1
k
Ax
k
2
(
3
:
145
)


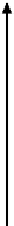






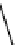






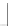



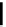
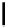


Search WWH ::

Custom Search