Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
RESIDUAL SPECTRA: FOURIER (FFT) − PADE (FPT); SIGNAL LENGTH N = 2048 (FFT), N/M (FPT, M = 1 − 32)
1.5
1.5
N/32 = 64
N/4 = 512
1
B
0
=4T
1
B
0
=4T
0.5
0.5
0
0
−0.5
−0.5
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N/32)
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N/4)
−1
−1
−1.5
−1.5
5
4
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
(i) Chemical shift (ppm)
(iv) Chemical shift (ppm)
1.5
1.5
1
N/16 = 128
B
0
=4T
1
N/2 = 1024
B
0
=4T
0.5
0.5
0
0
−0.5
−0.5
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N/16)
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N/2)
−1
−1
−1.5
−1.5
5
4
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
(ii) Chemical shift (ppm)
(v) Chemical shift (ppm)
1.5
1.5
1
N/8 = 256
1
N = 2048
B
0
=4T
B
0
=4T
0.5
0.5
0
0
−0.5
−0.5
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N/8)
FFT(N) − FPT
(−)
(N)
−1
−1
−1.5
−1.5
5
4
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
(iii) Chemical shift (ppm)
(vi) Chemical shift (ppm)
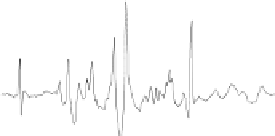
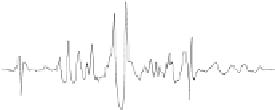
FIGURE 7.11
The residual absorption spectra Re(F)−Re(P
−
K
/Q
−
K
) for the partial FID of
human brain metabolites as computed by applying the FFT and FPT
(−)
to
the complexvalued time signal{c
n
}which has been encoded in Ref. [141] at
4T. The FFT is evaluated only with the full signal length N = 2048, whereas
the FPT
(−)
is computed at the partial signal lengths N/M(M > 1) with no
zero filling (N/32 = 64,N/16 = 128,N/8 = 256,N/4 = 512,N/2 = 1024) and
the full signal length N = 2048.












































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search