Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
TIME SIGNAL or FREE INDUCTION DECAY
ABSORPTION SPECTRA (PADE and FOURIER)
0.2
3
PADE: FPT
(+)
B
0
=7T
Real part of c
n
or FID
B
0
=7T
2.5
0.15
N = 2048
2
0.1
1.5
0.05
1
0
0.5
−0.05
0
−0.1
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
5
4
3
2
1
(i) Signal number n
(iv) Chemical shift (ppm)
0.2
3
PADE: FPT
(−)
B
0
=7T
Imaginary part of c
n
or FID
B
0
=7T
2.5
0.15
N = 2048
2
0.1
1.5
0.05
1
0
0.5
−0.05
0
−0.1
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
5
4
3
2
1
(ii) Signal number n
(v) Chemical shift (ppm)
3
1.5
Distribution of poles z
k
=e
i
τω
k
FOURIER: FFT
B
0
=7T
2.5
1
N = 2048
2
0.5
FPT
(+)
Convergence
region:
|z| < 1
1.5
0
1
−0.5
0.5
−1
FPT
(−)
Convergence region: |z| > 1
0
−1.5
−1
0
1
5
4
3
2
1
(iii) Re(z
k
)
(vi) Chemical shift (ppm)
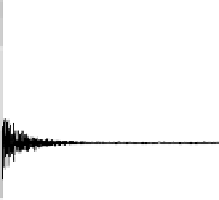
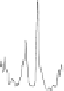
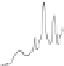
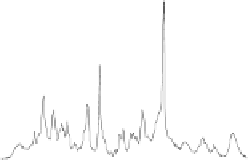
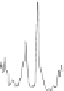
FIGURE 7.2
The real and imaginary parts of the complexvalued FID as encoded by Tkac
et al. [141] at 7T from occipital grey matter of a healthy volunteer: panels (i)
and (ii). Each FID point is divided by 2048×10
3
. Resonances in the FPT
(+)
and FPT
(−)
are seen to lie inside and outside the unit circle on panel (iii), as
symbolized by small circles and squares with the dots in their centers. The
absorption spectra at 7T computed using the FPT
(+)
, FPT
(−)
and FFT with
the full FID (N = 2048) are depicted on panels (iv), (v) and (vi), respectively.













































































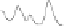













































































































































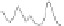


Search WWH ::

Custom Search