Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The dependence
(R) is almost linear. Within the range of the considered
τ
0ef
= 0
nanotube sizes
τ
has a relatively low value, which indicates the smoothness of
the surface of carbon nanotubes.
0ef
= 0
4.4 THE FLOW OF FLUID WITH AN EMPTY INTERLAYER
The works of Kotsalis et al. [35] and Xi Chen et al. [80] were analyzed in the
aforementioned analysis of the structure of liquid flow in carbon nanotubes. The
results of the calculations of the cited works (Figs. 4.16 and
4.17)
showed that
during the flow of the liquid particles, an empty layer between the fluid and the
nanotube is formed. The area near the walls of the carbon nanotube
R
≤
r
≤
R
∗
becomes inaccessible for the molecules of the liquid due to van der Waals re-
pulsion forces of the heterogeneous particles of the carbon and water (
Fig. 4.2)
.
Moreover, according to the results of Kotsalis et al., [35] and Xi Chen et al. [80]
R
≤
r
≤
R
thicknesses of thelayers
regardless of radiuses of the nanotubes are
∗
practically identical:
∗
R
0,88.
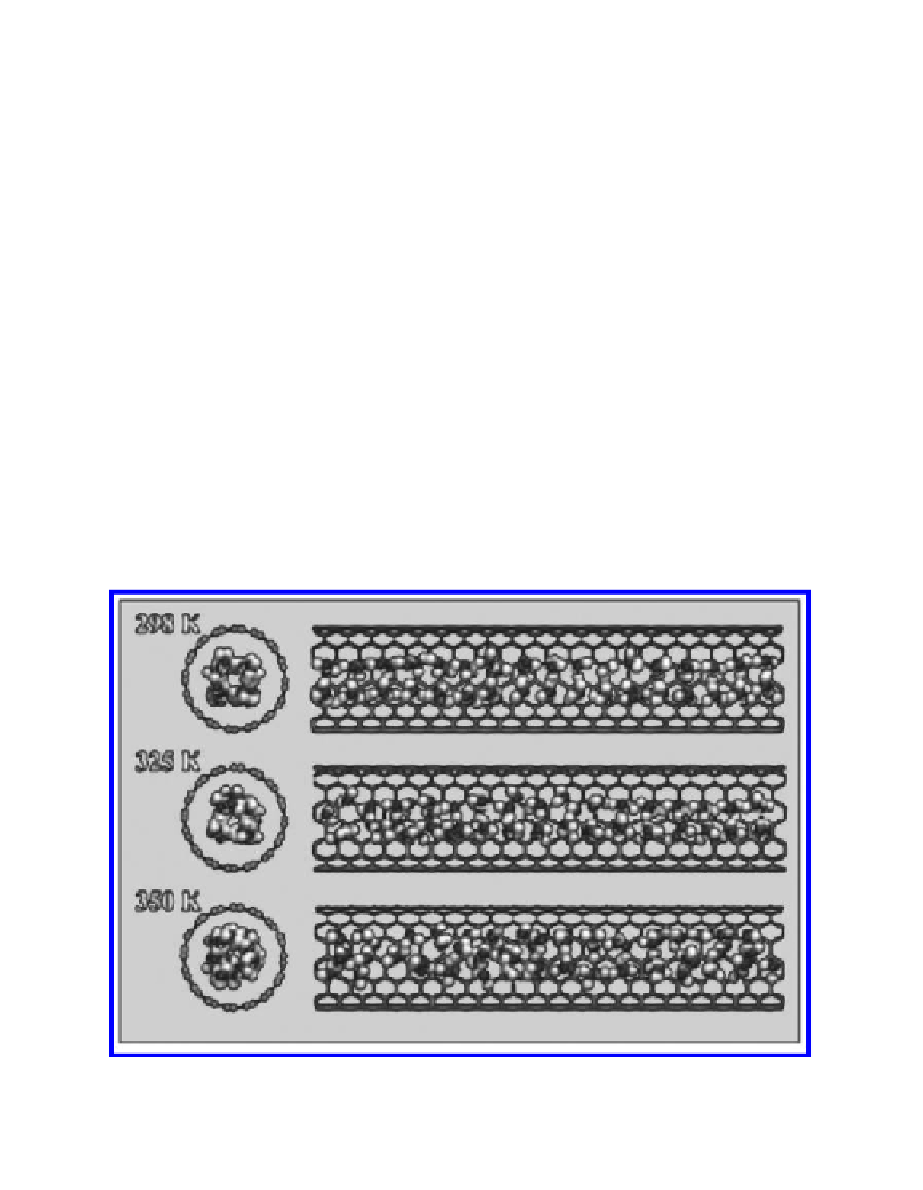
A similar result was obtained in Hongfei Ye et al.[26], which is an image Fig.
4.16 of the configuration of water molecules inside (8, 8) single-walled carbon
nanotubes at different temperatures: 298, 325, and 350°K.
/ ≈
FIGURE 4.16
The configuration of water molecules inside single-walled carbon
nanotubes.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search