Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
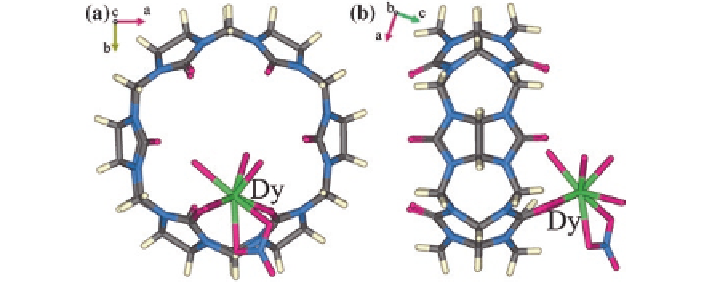
Fig. 4.1
Top and side views of the molecular structure of the complex of Q[6]/Dy
3
+
In a recent study a simple 1:1 (Dy:Q[6]) complex, [Dy{Q[6](NO
3
)(H
2
O)
4
}]
(NO
3
)
2
nH
2
O (
n
=
6 or 7) (Fig.
4.1
), was prepared and its magnetic properties were
investigated [
7
]. This complex displays single-ion magnet behavior with two slow
magnetic relaxation processes. The latter is sensitive to the degree of solvation present.
Changes in solvation can induce the slow magnetic relaxation of this compound to
switch between the temperature-independent and the temperature-dependent regimes.
More recently, we used the strategy to synthesize Q[7]-based coordina-
tion polymers by introducing [M
trans
Cl
4
]
2
−
anions as structure directing
agents into the Q[7]-M
alkaline earth
systems. The structure directing effect of the
[M
trans
Cl
4
]
2
−
anions not only appears in the construction of novel Q[
n
]/metal
ions-based coordination polymers but can also result in the formation of Q[
n
]-
based novel supramolecular assemblies, such as the mentioned honeycomb-like
frameworks [
4
,
5
]. The proposed driving forces of the structure directing effect
of the [M
trans
Cl
4
]
2
−
anions are ion-dipole interactions and hydrogen bond-
ing between the [M
trans
Cl
4
]
2
−
anions and
≡
CH or
=
CH
2
groups on the back of
the Q[8] molecules. The solid state structures, as determined by X-ray crys-
tallography, show that compounds {Ca
2
(H
2
O)
4
(Q[7])}2[CdCl
4
]22H
2
O and
{Sr
3
(H
2
O)
16
(Q[7])
2
}4[CdCl
4
](H
3
O)
2
36H
2
O exhibit similar coordination features
and supramolecular assemblies, in which [CdCl
4
]
2
−
anions surround a Q[7] mol-
ecule through: (1) the dipole interaction between portal carbonyl carbons with
Cl from [CdCl
4
]
2
−
anions, and (2) the unusual hydrogen bonding of Cl from
[CdCl
4
]
2
−
anions with methine or methylene on the back of the Q[7] molecules.
Generally, Q[7] molecules rarely coordinate with common metal ions to form sta-
ble Q[7]/Metal complexes, in particularly, the coordination polymers. However,
with a negative [CdCl
4
]
2
−
anion ring, which attracts positively charged species,
Q[7] molecules are ready to coordinate with metal ions. The “honeycomb effect”
of [CdCl
4
]
2
−
anions result in the formation of one-dimensional coordination poly-
mers (Fig.
4.2
a-c) [
8
]. Moreover, These Q[7]-based coordination polymers present
remarkable selective sorption properties for separation. The M
alkaline
-Q[7]-based
coordination polymers were used as an extraction coating on solid-phase micro-
extraction (SPME) fibers to examine their usefulness for separation. The SPME
Search WWH ::

Custom Search