Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
agents [
35
,
48
,
49
]. In previous studies, there have been numerous attempts to
grow single crystals of complexes in which lanthanide cations are coordinated to
Q[7] in various acidic media, but all have proved unsuccessful. However, when
transition metal ions are introduced into HCl solutions containing Q[7] and Ln
3
+
salts, Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based linear coordination polymers are readily produced, and
the transition metal cations in the form of the tetrachloride ([MCl
4
]
2
−
) may be
arranged into honeycomb-like hollows. These hollows can then accommodate the
Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based linear coordination polymers through ion-dipole and C-HCl
interactions coupled with metal coordination, as shown in Fig.
3.11
f. We first dem-
onstrated the synthesis of a series of Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based linear coordination poly-
mers in the presence of [CdCl
4
]
2
−
anions [
47
]. Subsequent studies have revealed
that a few transition metal ions, such as Zn
2
+
, Cu
2
+
, and Co
2
+
, in the form of tet-
rachloride anions [MCl
4
]
2
−
, may also play a similar role in triggering the forma-
tion of 1D Ln
3
+
-Q[
n
] coordination polymers [
41
,
48
,
49
].
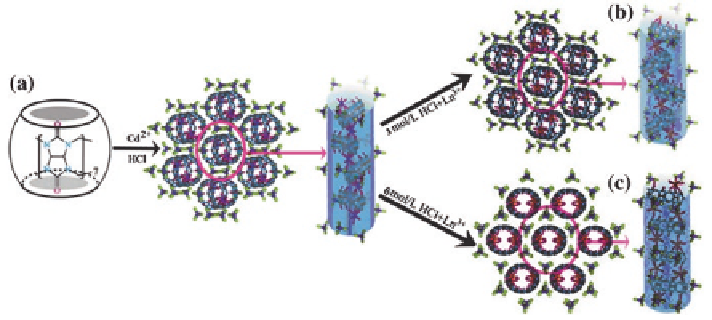
Because of the similar chemical properties of the lanthanides, the interactions
of various lanthanide cations with Q[7] molecules give rise to similar coordina-
tion features and supramolecular assemblies. Interestingly, the shapes of the 1D
Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based coordination polymers could be finely tuned by the lanthanide
metal ions under high concentrations of acid in the presence of [CdCl
4
]
2
−
dianions
[
35
]. As shown in Scheme
3.4
, lanthanide cations coordinated with Q[7] to form
zigzag channels in less acidic media (<3.0 mol/L HCl) (Scheme
3.4
b). However,
in more acidic media (>3.0 mol/L) tubular channels formed (Scheme
3.4
c).
Figure
3.28
shows the common structures of Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based zigzag and tubu-
lar structures. The former has alternating Q[7] molecules and Ln
3
+
cations at 1:1
ratio; the latter has alternating Q[7] molecules and Ln
3
+
cations at 1:2 ratio.
The crystal structures in both cases also reveal that the [CdCl
4
]
2
−
dianions
surround each Q[7] molecule in the coordination polymer via ion-dipole interac-
tions between the portal carbonyl carbon atoms (O
=
C
ʴ+
Cl
−
-CdCl
3
−
) and the
chlorine atoms of the anions, as well as hydrogen bonding between the chlorine
Scheme 3.4
Zigzag and tubular channels construction from Q[7]/Ln
3
+
-based coordination poly-
mers in the presence of [CdCl
4
]
2
−
dianions
Search WWH ::

Custom Search