Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
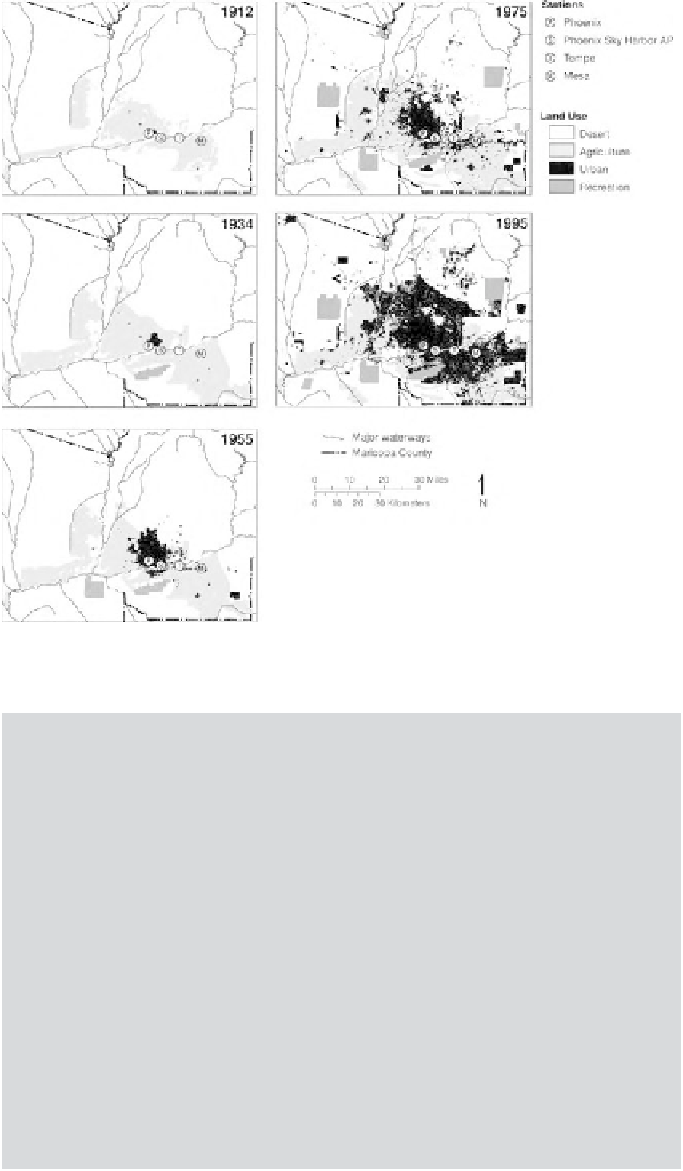
Figure 7.8 Land use
change for Phoenix region,
Arizona, USA, showing the
shift from desert (natural)
and agriculture (human
modified) to urban from
1912 through 1995. Notice
how the land use changes
around the climate stations
through time. (After Brazel
et al.
2000
)
reference, the urban area may appear hotter (irrigated reference) or cooler
(desert reference) than the surrounding rural sites. Moreover, in studies that
look at the development of the UHI with time, it is important to recognize that
the surface and thermal properties of both cities and their rural surroundings
change through time. Brazel et al.(
2000
), in a study of Phoenix, Arizona,
document landscape changes (Figure
7.8
) both within and around the city
(irrigation and intensification of agriculture) that impact urban-rural differ-
ences in temperature.
7.3.4 The surface energy balance
Ultimately urban climate effects are due to differences between the city and
its pre-existing landscape surface characteristics. Thus understanding, pre-
diction, and mitigation of urban climate effects are intricately tied to knowl-
edge of surface-atmosphere exchanges in urban environments. A powerful
framework for studying urban climate effects, and their relations to the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search