Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
IG
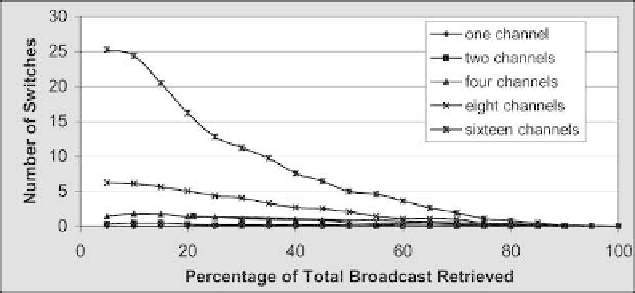
. 31. Channel switching frequency (
Top Down Retrieval Scheme
).
when the
top down retrieval scheme
is employed. The maximum number of channel
switches is reached for when size of a user query is less than 5%. At this point, the
number of broadcast passes approaches the number of channels, thus mimicking the
access pattern of the
Row Scan
Method. In short, the
top down retrieval scheme
does
not allow the number of broadcast passes to exceed the number of channels, and thus
as the number of requested data elements increases, the number of channel switches
decreases.
7.2.3.3 Energy Consumption.
In general, the energy consumption fol-
lows the same pattern as the channel switching frequency. For the
bottom up retrieval
scheme
, the energy consumption is dominated by the number of channel switches.
As a result, the energy consumption increases as the number of channels increases. In
addition, the energy consumption increases, up to a threshold point, as the number of
requested data elements increases, and then it decreases as the number of requested
data elements continues to increases (
Fig. 32
).
Figure 33
depicts the energy consumption of the
top down retrieval scheme
.The
figure illustrates that the energy consumption increases as the number of data ele-
ments being retrieved increases. The increase in energy consumption follows a linear
trend that is directly related to the increase of data elements requested. This is be-
cause the retrieval of a data element implies the active operational mode. In addition,
the
top down retrieval scheme
attempts to minimize the channel switching frequency.
As a result, the energy consumption is dominated by the number of requested data
elements.