Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
T
ABLE
VI
I
MPROVEMENT OF THE
B
OTTOM UP
R
ETRIEVAL
S
CHEME VS
.
THE
R
OW
S
CAN
(10 O
BJECTS
R
EQUESTED
)
# of channels
# of passes
Response time
Energy
2
48.0%
28.0%
2.7%
4
68.0%
43.6%
3.1%
8
72.3%
46.5%
3.3%
16
71.8%
40.8%
3.4%
However, relative to the
Row Scan
algorithm, one should also consider the ex-
pected overhead of the proposed retrieval schemes. The simulation results showed
that in the worst case, the overhead of
retrieval scheme1
was slightly less than the
time required to transmit one data page.
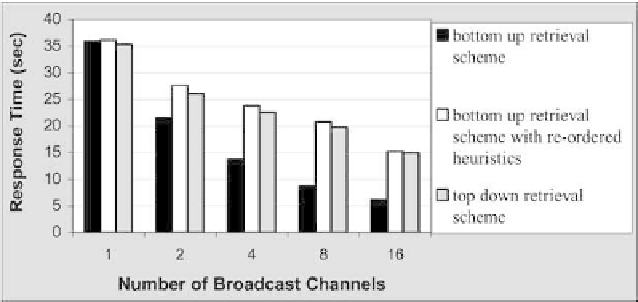
7.2.3.1 Response Time.
The simulation results showed that, regardless
of the underlying retrieval protocol, the response time decreases as the number of
channels increases. In addition, the response time increases as the number of re-
quested data elements increases. Finally, for all cases,
top down retrieval scheme
(see
Section
3.6.2
), relative to the
bottom up retrieval scheme
compromises the response
time (
Fig. 29
)—the additional time requirement can be associated to the goal of re-
ducing channel switches during the retrieval, thus incurring more broadcast passes
that inherently increase the access latency. From
Fig. 29
it can be observed that the
least-cost path technique is more efficient in generating the access patterns than the
technique used in the
bottom up retrieval scheme
.
F
IG
. 29. Response times comparison for different retrieval protocols.