Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
IG
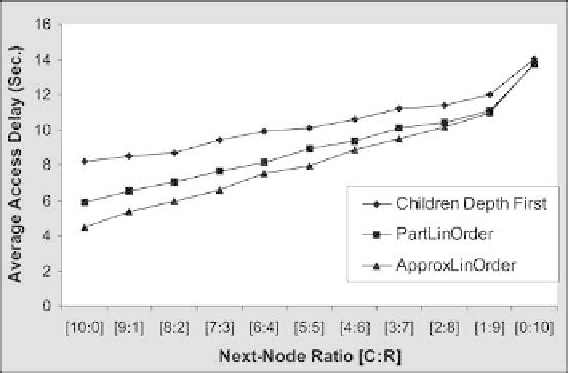
. 16. Access delay vs. next-node ratio.
The simulation results showed that in general, the average access delay is reduced as
more connectivity is injected in the access graph.
In separate simulation runs, the simulator also measured the effect of varying the
percentage of popular objects and the replication frequency. As one can note, these
two parameters have the same effect on the total number of objects on the air channel,
though from the access pattern perspective, the semantic of the accesses are different.
In both cases, the average access delay increased as either parameter increased. The
average access delay for different degrees of connectivity among objects was also
observed and measured. The average access delay for objects connected through
strong connections was about 4.3 seconds, whereas it was 7.3 and 7.6 seconds for
normal and weakly connected objects, respectively. As would be expected, these
results show that the improvement is considerable for the objects connected by a
strong connection but for a normal connection the performance was close to that
of the weak-connection case since the algorithm performs its best optimization for
strongly connected objects.
4 . 4
S e c t i o n C o n c l u s i o n
In this section two heuristically-based mapping algorithms were discussed, sim-
ulated, and analyzed. Performing the mapping in polynomial time was one of the
major issues of concern while satisfying linearity, locality, and replication of popular