Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
IG
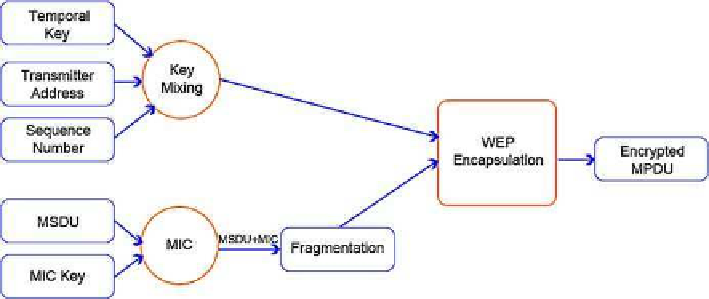
. 6. Graphical diagram of TKIP Encapsulation. Note: MSDU is the MAC Service Data Unit and
MPDU is the MAC Protocol Data Unit.
address, which is then mixed with a sequence number to produce a key that is used
as input to the previous WEP algorithm. By adding all the extra steps the key is now
much more secure against attack because it now depends on time and the sender's
MAC address. TKIP also uses a sequence counter to prevent replay attacks and a
Message Integrity Check (called MIC or Michael) to prevent message modification.
Along with the sequence number, the source and destination addresses are added.
Michael is also a one-way hash function rather than a simple linear CRC. This adds
security to the algorithm because integrity verification is extremely difficult to forge.
Figure 6
provides a graphical representation of TKIP
[13,18]
.
More recently, the Wi-Fi alliance has announced the ratification of WPA2 which
completely stops the use of WEP as an underlying protocol. Instead it uses the much
stronger AES algorithm. As of this writing, WPA2 using AES does not share the
same vulnerabilities as the original WPA.
3 . 1 T h e W PA - P S K A t t a c k
There are two primary ways that TKIP can be used. The more secure way is to use
802.1x to distribute the keys and keep track of key management. The other way is to
provide the client and access point with the same pre-shared key which is used as the
pairwise master key (PMK) in the TKIP process. Although this shares many of the
key management problems that WEP had, it does offer some “security through ob-
scurity.” One of the problems with TKIP is that if an attacker can determine what the
PMK is for any one of the wireless clients, he or she can gain access to the network.
Researcher Robert Moskowitz discovered a problem with the WPA-PSK imple-
mentation when short passphrases are chosen
[10]
. When a pre-shared key is used,