Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
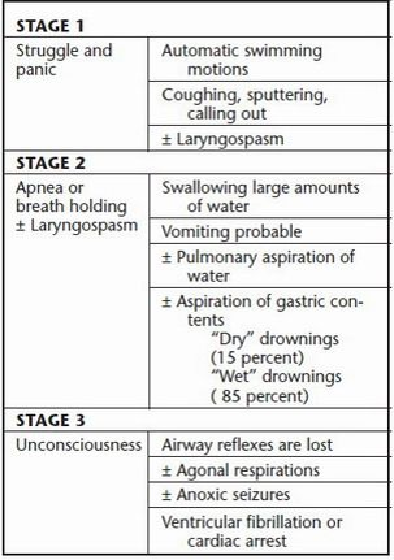
Table 28-1
Stages of Drowning
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DROWNING
The common pathway for organ system failure, morbidity, and mortality is reduced blood
oxygen concentrations (hypoxemia). The sequence of events (
Table 28-2
)
is typically an
initial period of panic and struggle with breath holding. Subsequently water is inhaled.
Once asphyxia occurs, the person becomes unconscious and water passively enters the air-
waysasairwayreflexesdisappear.Cardiopulmonaryarrestfollows.Irreversiblebraindam-
age may occur in as little as six minutes.
Electrolyte Abnormalities
In both saltwater and freshwater drowning, blood concentrations of electrolytes (sodi-
um, potassium, chloride, and carbon dioxide) are usually normal. In freshwater drowning,
elevated potassium concentrations may result from breakdown of red blood cells (lysis.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search