Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
pain of pleural involvement may be absent if the blood clot lodges in a central part of the
lung.
A large pulmonary embolus can produce cardiovascular collapse and death within
seconds. Smaller emboli cause respiratory difficulty, including shortness of breath, de-
creased exercise capacity, and sometimes hypoxia that may be more pronounced at high
altitude.
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism
Prevention of pulmonary embolism is important but difficult. Everyone confined to a
tent by a storm should change position and exercise their feet and legs for a few minutes
everyhour.Constricting clothing shouldberemoved.Long-distance airline passengersand
persons hospitalized postoperatively often wear snug elastic stockings that come up to the
knee, but these are of doubtful benefit and would be impractical in the wilderness. Extra
fluids are essential at altitude where dehydration promotes venous thrombosis, as well as
hypothermia and other problems. An aspirin a day may help prevent venous thrombosis at
high altitude because it inhibits platelet aggregation.
Treatment of Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
Treatmentofvenousthrombosisandpulmonaryembolismisthesame.Bothinitiallyre-
quire anticoagulant drugs that are administered intravenously (heparin) or subcutaneously
(enoxaparin), followed by several months of oral therapy with warfarin. Heparin and war-
farin need to be closely monitored to prevent too much anticoagulation that might cause
seriousbleedinginthegastrointestinaltractorbrain.Therefore,treatmentofvenousthrom-
bosis or pulmonary embolism requires evacuation to a medical facility. Moderate anal-
gesics are usually adequate for pain.
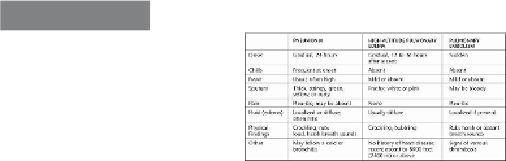
Table 18-1
Features of Various Pulmonary Disorders
Once venous thrombosis develops, the individual should be immobilized. Walking or
other movement may cause the clots to break off and embolize. The feet should be elev-
atedslightly,andawkwardpositionsshouldbeavoided.Asnug,butnottight,elastic band-
age wrapped around the leg from toes to knees is thought by some to decrease the risk of
embolism and is unlikely to worsen matters. Evacuation is essential, especially if pulmon-
ary embolism has occurred. During evacuation the individual should be carried as much as
Search WWH ::

Custom Search