Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
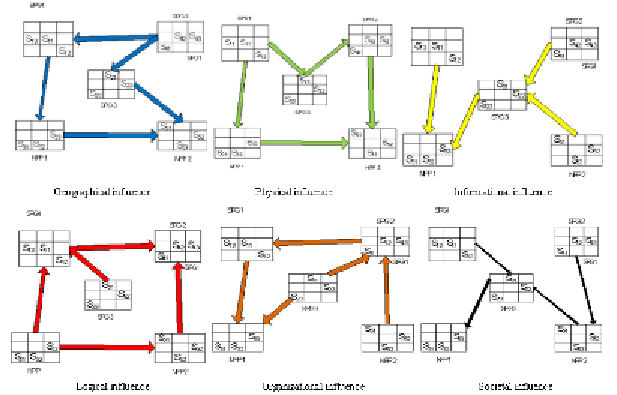
Figure 12. Fragments of six BBNs for different types of influence
empirical developments in CWW can be found
in (Zadeh, 2001).
The linguistic approach based on fuzzy sets
has given very good results for qualitative risk-
analysis of critical information control system
based on FMECA. It is an approximate technique
in its essence, which represents qualitative as-
pects as linguistic values by means of linguistic
variables, that is variables whose values are not
numbers but words or sentences in a natural or
artificial language.
The fuzzy linguistic approach deals with quali-
tative aspects that are represented in qualitative
terms by means of linguistic variables. When a
problem is solved using linguistic information, it
implies the need for CWW. Here, an important
limitation for this approach appears, because the
computational techniques used in the specialized
literature present a common drawback, the “loss
of information,” that implies a lack of precision
in the final results.
These computational techniques are as follows.
The first one is based on the extension principle
(Brezhnev, 2010). It makes operations on the
fuzzy numbers that support the semantics of the
linguistic terms.
The second one is the symbolic method. It
makes computations on the indexes of the lin-
guistic terms.
In both approaches, the results usually do not
exactly match any of the initial linguistic terms,
then an approximation process must be devel-
oped to express the result in the initial expres-
sion domain. This produces the consequent loss
of information and hence the lack of precision
(Bowles, J. B., 2004).
As mentioned above many aspects of risk
analysis process cannot be assessed in a quanti-
tative form, but rather in a qualitative one, i.e.,
with vague or imprecise knowledge. In that case,
a better approach may be to use linguistic assess-
ments instead of numerical values. The variables,
which participate in these problems, are assessed
by means of linguistic terms. This approach is
adequate in some situations, for example, when
attempting to qualify phenomena related to hu-
man perception, we are often led to use words in
natural language.
The use of linguistic assessments implies to
make computations with them.
For example, a set of seven terms S could be
given as follows:
Search WWH ::

Custom Search