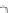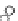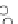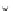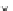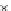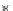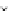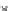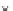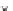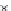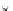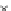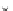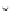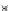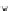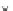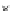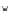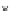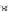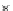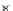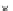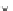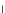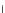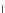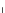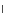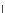Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
0.4
2
x
2
^
E
(e)
0.3
1
0
0.2
−1
0.1
−2
x
1
e
0
−2
0
2
−2
−1
0
1
2
Error Rate (Test) = 0.067
1.5
0.8
Error Rate
^
S
1.4
0.6
1.3
0.4
1.2
0.2
epochs
epochs
1.1
0
0
20
40
60
0
20
40
60
Fig. 3.24 The final converged solution of Example 3.11. The downside graphs of
the Shannon entropy and the error rate (solid line for the training set and dotted
line for the test set) are in terms of the no. of epochs.
0.25
Error rate
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
n
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
Fig. 3.25 Learning curves for the ring dataset of Example 3.11. The learning
curves were obtained by exponential fits to the
P
ed
(
n
)
(denoted '+') and
P
et
(
n
)
(denoted '.') values. The shadowed region represents
P
ed
± s
(
P
ed
)
; the dashed lines
represent
P
et
± s
(
P
et
)
.
3.4.2 Theoretical and Empirical MEE in Realistic
Datasets
We follow the same procedure as in Sect. 3.3.2.2, applying the learning algo-
rithm
of
the
hypersphere
neuron
(in
fact,
the
circle
neuron)
with