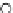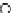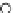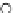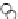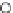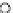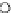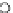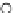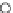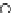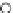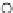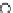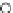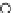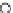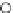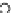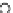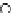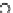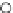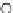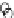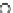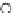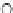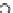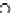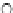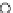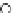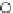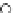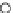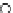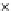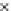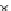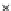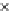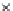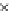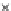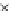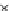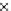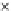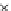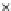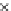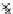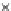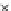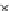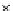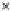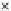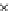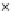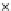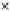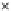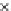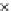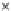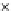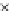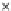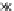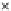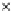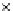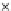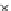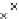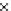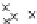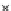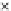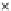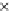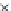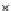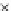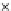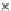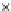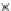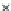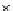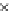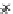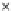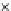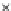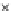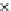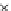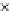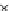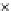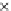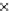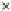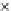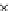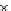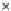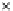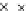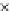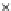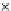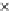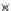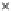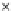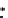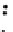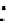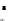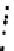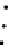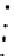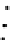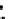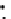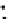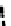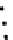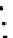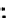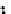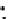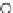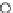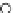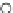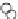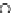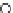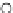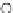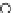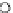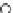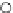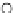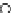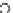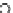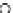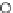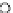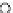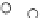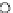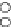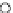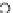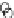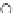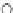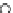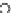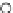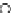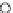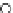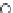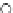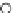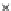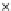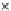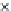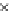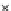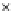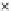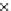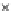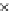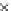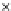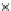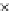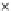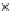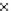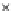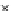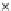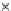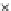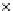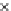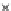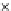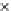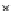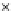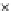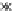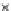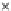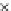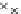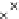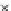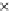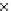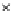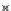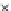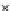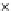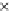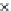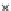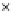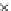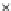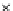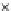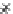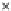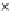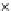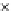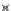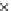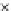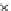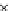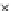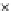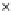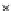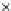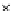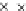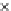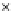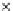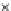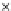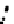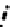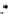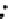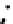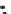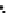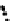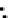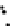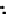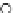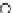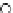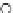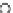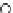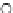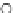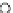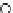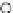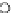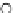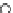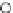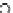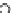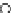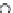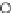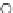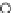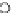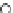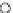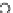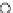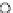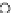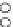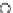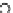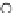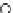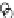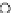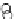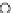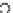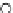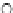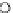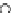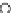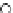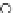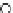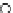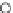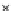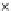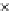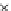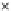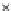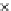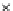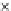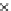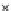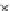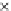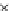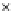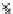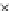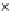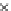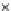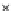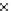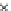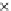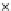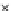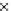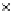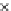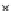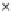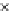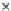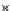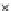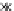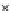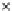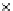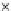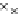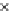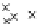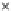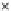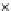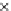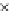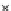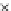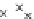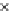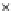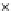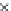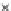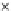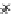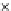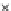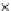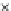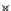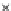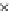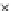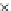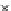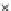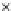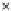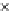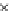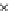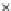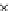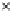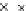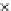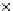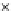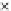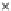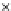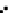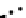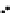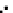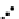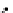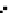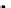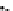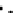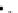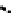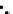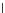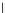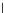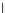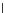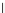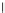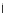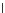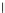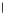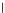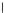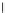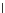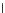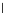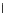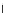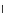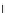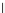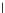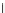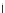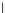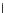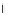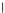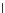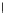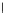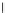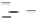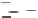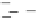Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
0.235
x
2
^
E
(e)
2
0.23
0
0.225
0.22
−2
x
1
e
0.215
−2
0
2
4
−2
−1
0
1
2
(a) Epochs=0
0.26
x
2
^
E
(e)
2
0.24
0
0.22
−2
x
1
e
0.2
−2
0
2
4
−2
−1
0
1
2
(b) Epochs=20
0.4
x
2
^
E
(e)
2
0.3
0
0.2
−2
x
1
e
0.1
−2
0
2
4
−2
−1
0
1
2
(c) Epochs=30
Fig. 3.8 The Gaussian two-class dataset at different iterations of the MEE percep-
tron. The left graphs show the dataset with the linear decision border (solid line).
The right graphs show the error PDF in the
E
=[
−
2
,
2]
support.
Figure 3.8 shows the evolution of the decision border and the error PDF
(computed only at the
e
i
values) at successive epochs. Epochs =0is the initial
configuration, with random weights and bias. Note the evolution towards a
monomodal error PDF.
Figure 3.9 shows the final solution, corresponding to a converged behavior
of the algorithm to low entropy and error rates. This solution has
P
ed
=0
.
213
and
P
et
=0
.
227. The value of the min
P
e
for this problem is
0
.
228.The
P
e
Bayes
is smaller since it is well-known that it can only be achieved with a
quadratic decision border.
≈