Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
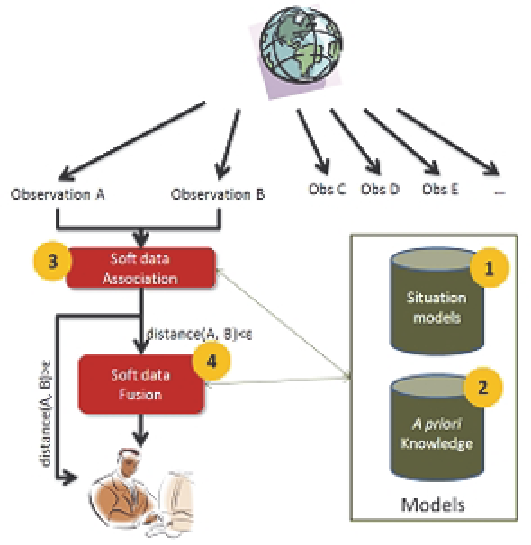
Soft data fusion
is depicted by (4) on Figure 4. When two observations are compatible and (at
least partially) overlap, the multi-source information synthesis aims at building an unique
view of the observed situation from them.
Fig. 4. General approach for situation recognition
In the remaining parts of this chapter, we emphasize on the modeling, association and fusion
phases of soft observations that are not uniformly reported.
4. Domain knowledge and semantic representations
Domain knowledge has a major role within data and information fusion. Therefore, there is
a need to express domain knowledge in a unique way, regardless of the different sources of
information.
Furthermore, the data or information items acquired through the different sources are
combined with this domain knowledge through the information process which produces new
information items. This stresses the importance of having a unique formalism for knowledge
representation that can also be used to represent and store the data and information that will
be processed through fusion. The semantic used for representing the knowledge has to be
shared between data and information as well.
4.1 Semantic networks
Within Artificial Intelligence, semantic representation formalisms were first developed in
order to represent, store and automatically analyze the content of natural language.
Semantic nets (or Semantic networks) are graphical representations of interrelated concepts. A
semantic network represents a taxonomy of concepts (or objects), denoted by the nodes of the
network, and their properties, represented by the edges of the network. Two kinds of nodes

Search WWH ::

Custom Search