Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
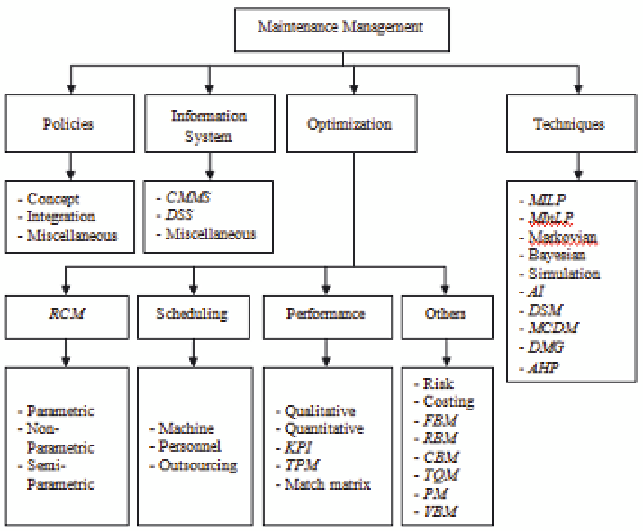
Abbreviation represent: CMMS: Computerized Maintenance Management System; DSS: Decision
Support System; RCM: Reliability-centred Maintenance; KPI: Key Performance Index; TPM: Total
Productive Maintenance; FBM: Failure-based Maintenance; RBM: Risk-based Maintenance; CBM:
Condition-based Maintenance; TQM: Total Quality Maintenance; PM: Preventive Maintenance; VBM:
Vibration-based Maintenance; MILP: Mixed Integer Linear Programming; MInLP: Mixed Integer non-
Linear Programming; AI: Artificial Intelligence; DSM: Decision Support Model; MCDM: Multiple
Criteria Decision-Making; DMG: Decision-Making Grid; and AHP: Analytical Hierarchical Process
Fig. 1. Sub-division Tree of Maintenance Management
4.1 Maintenance policies
Guy and Steve (1999) reviewed the general terms of maintenance. They studied
maintenance development and the reason behind it changing from time to time. After that,
they focused on the enhancement and evolution of information systems in maintenance.
Some important findings on enhancement of the development of information systems in
maintenance are given, as they have discovered that new strategic development in
maintenance is due to information system application and development.
Lam and Lin (2004) integrated some replacement policies into corrective maintenance.
Corrective or Failure-based Maintenance (FBM) is unscheduled maintenance or repair to
return the machine to a defined state. There are no interventions until a failure has occurred.
Lewis (1999) addressed corrective maintenance as reactive maintenance, where any
emergency breakdown will lead to a bigger impact on the operation. Since the failures are
unplanned, they might result in a big loss to the organization in terms of cost and time.
Therefore, a better maintenance concept must be introduced to prevent this unplanned
downtime and reduce the cost of the failure. The breakdown maintenance concept is still
applied to equipment that is not mission critical and where the downtime would not affect
the main operation of the organization, such as light bulbs and consumable parts. Lam and
Lin (2004) have introduced some numerical methods and designed optimal replacement
policies in FBM.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search