Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
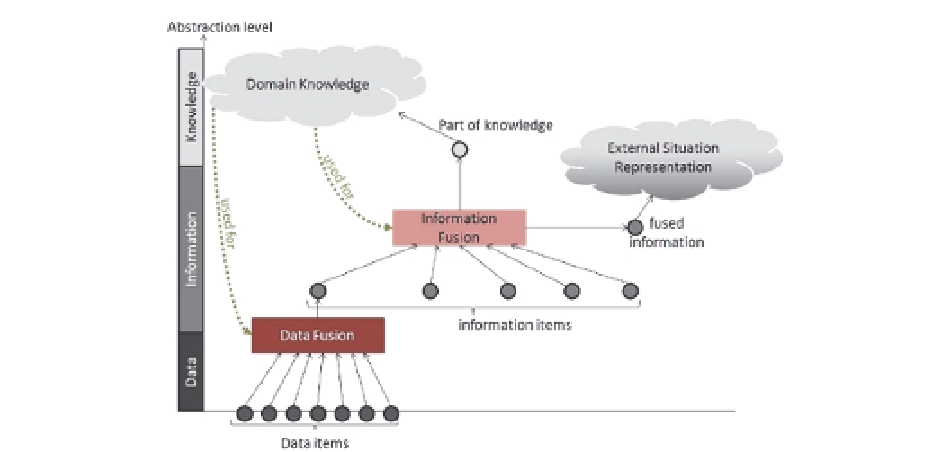
Fig. 1. Role of data, information and knowledge in the fusion process
humans, it is classified as information and knowledge according to the definitions given
above.
The necessity of taking into account high-level information, which is also called "soft data"
has recently been reported by the information fusion community. As stated in Pravia et al.
(2008), under some circumstances, physics-based sensors are not as effective in the detection
of people and complex activities for instance. In these situations, soft information sources
are critical. The ability to express observed relationships is of importance for decision support
systems, for inference purpose. However, most electronic sensors are feature based and do not
generally provide information on relationships. Therefore, the study of soft data is of major
importance.
Soft data items detections are typically qualitative, open to interpretation, and often outright
inconsistent. These properties make the mathematical modeling of soft data very challenging.
Studies such as Sambhoos et al. (2008), Petersen (2004) and Godbillon-Camus & Godlewski
(2007) analyze the characteristics of soft and hard data, in order to clearly distinguish them.
Three types of dimensions emerge from these studies:
Nature:
hard information is quantitative - “numbers” (in finance these are balance sheet
data, asset returns ...); soft information is qualitative - “words” (opinions, ideas, projects,
comments ...); hard information is also rather “backward looking” (e.g. balance sheet data)
as soft information is rather “forward looking” (e.g. business plan).
Collecting method:
collection of hard data does not depend upon the context of its
production, while collecting soft information includes its production context.
Cognitive factors:
subjective judgment, opinions and perception are absent
in hard
information, whereas they are integral components of soft information.
Recent studies such as Buford et al. (2008), Sambhoos et al. (2008) and Laskey (2008) insist
on the importance of such information for situation awareness and other decision support
issues in general. They propose new approaches for information fusion, taking into account
observations provided by humans.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search