Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Rural
Time
Semi-urban
Time
Urban
Time
Figure 1.3
A comparison of stormwater runoff rates versus time for rural, semi-urban, and urban
conditions. Urban areas experience intense runoff rates with high fl ows over short periods
of time. Illustration by Shawn Kavon.
a variety of pollutants—fertilizers, pesticides, bacteria, sediment, nutri-
ents, oils and greases, metals, organic matter, toxic chemicals, trash and
debris—from rooftops, streets, and sidewalks and discharges them into
waterways. Landscape theorist Michael Hough writes, “The benefi ts of
well-drained streets and civic spaces are paid for by the costs of eroded
stream banks, fl ooding, impaired water quality and the disappearance of
aquatic life.”
56
The logic of effi cient conveyance of urban runoff is at odds
with contemporary calls for environmental protection.
57
Today, the most widely used strategy to manage stormwater volumes
is detention ponds. Detention ponds were originally developed to control
































































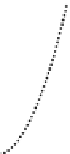









Search WWH ::

Custom Search