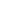
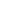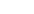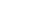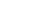Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
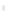
-4
+1
-3
-1
+1
-5
D
aylight saving
not observed in
Saskatchewan
and parts of
British Columbia,
Ontario and
Québec
ALASKA
STANDARD
TIME
-7
Arctic Circle
+11
+12
+7
+9
UNIVERSAL TIME
CO-ORDI
NA
TE
(UTC) /
GREEN
W
ICH
MEAN TIME
(GMT)
-9
ATLANTIC
STANDARD
TIME
+10
+4
+3
+5
-4
NEWFOUNDLAND
STANDARD
TIME
CENTRAL
EUROPEAN
TIME
+2
1
2
EASTERN
STANDARD
TIME
-3
+6
+4
+1
PACIFIC
STANDARD
TIME
MOUNTAIN
STANDARD
TIME
-3
ALEUTIAN/
HAWAII
STANDARD
TIME
-5
+4
-8
-7
CENTRAL
STANDARD
TIME
-10
+9
-1
+8
UTC
-4
1
2
+4
-6
+3
1
2
-11
+5
+5
3
4
Daylight saving
not observed in
Arizona and most
of Indiana
Tropic of Cancer
-5
+6
+5
1
2
1
2
-1
+4
+6
UTC
+1
+2
-5
-4
+10
-4
+7
+3
+12
3rd OCTOBER 2005
Annular solar eclipse
+6
+10
+11
+9
-6
+5
+8
+8
Equator
+4
+7
+1
0
+12
+
13
+14
UTC
+5
-5
-3
8th APRIL 2005
Hybrid solar eclipse
(Annular and total along
diferent sections of its path)
+9
+11
-9
1
2
-4
+3
1
2
+7
+6
-10
+12
UTC
-10
+11
-2
CENTRAL
STANDARD
TIME
-11
+3
+4
-10
+13
+1
-9
Tropic of Capricorn
EASTERN
STANDARD
TIME
WESTERN
STANDARD
TIME
+8
-9
+9
1
2
+2
+12
1
2
+11
-6
+10
-4
The term GMT (Greenwich
Mean Time) has been
generally replaced by UTC
(Universal Ti
m
e Co-ordinate),
although the times are the
same and it is still known as
GMT in the UK and USA.
UTC is used throughout the
world for marine and airline
navigation.
1
2
+10
GMT
+5
-3
H
OURS BEHIND UTC
HOURS AHEAD OF UTC
+12
3
4
+12
Centre lines of solar eclipses in 2005
+3
+3
Areas where daylight saving is observed
(clocks put forward one hour
:
-4
GMT
+5
-2
Northern hemisphere (+1hr from
March/April - September/October)
Southern hemisphere (+1hr from
September/October - February/March)
-2
HOURS OF DAYLIGHT AND THE SEASONS
THE SUN AND THE EARTH
PHASES OF THE MOON
SOLAR ECLIPSE
Northern hemisphere
Southern hemisphere
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
Latitu
de:
Excludes twilight, which lasts
approximately 20 minutes before
sunrise and 20 minutes after
sunset at the Equator. This time
increases to 30 minutes at 30˚ N
or S and 40 minutes at 50˚ N or S.
Sun directly overhead
at noon over Tropic of
Cancer
21 June
(approx.)
:
Summer solstice (NH)
Winter solstice (SH)
Equator
20˚
40˚
60˚
80˚
New moon
SUN
W
I
N
T
E
R
SPRING
SUMMER
A
U
T
U
M
N
S
U
M
M
E
R
AUTUMN
(FALL)
WINTER
S
P
R
I
N
G
(FALL)
1 July: Aphelion
(earth furthest from sun)
152m km (94.5m miles)
Maximum
width of total
eclipse on the
earth's surface:
269 km
(167 miles)
Day
Night
Last
quarter
23 Sept
(approx.)
:
Autumnal
equinox (NH)
Vernal
equinox (SH)
21 Mar
(approx.)
:
Vernal
equinox (NH)
Autumnal
equinox (SH)
Northern
hemisphere
21 Mar
21 Jun
23 Sep
22 Dec
Southern
hemisphere
23 Sep
22 Dec
21 Mar
21 Jun
SUN
EARTH
Average
distance:
384,400 km
(238,860 miles)
Umbra
(total eclipse
on earth)
Penumbra
(partial eclipse
on earth)
First
quarter
1 Jan: Perihelion
(earth closest to sun)
147m km (91.4m miles)
1
2
3
4
Vernal equinox
Summer solstice
(longest day)
Autumnal equinox
Winter solstice
(shortest day)
North Pole
Moon as
viewed
from earth
MOON
22 Dec
(approx.)
:
Winter solstice (NH)
Summer solstice (SH)
Full moon
EARTH
Sun directly overhead
at noon over Tropic of
Capricorn
1
2
3
4
3
4
1
2
NH:
Northern hemisphere
SH:
Southern hemisphere
Sizes and distances are not to scale
An annular eclipse occurs when the apparent
size of the moon is too small to fully cover the
disc of the sun, resulting in a ring of sunlight
remaining around the moon
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec