Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
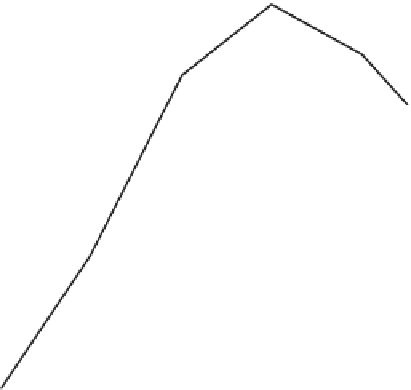
Destinations too go in and out of fashion. The product
life cycle concept suggests that all products go through
similar stages during their useful life, as shown in Figure
5.4.
FOCUS ON INDUSTRY
BRANDING AT BRITISH AIRWAYS
'British Airways' is the company's primary brand and
it is used to create a certain expectation about the
products and services that people will experience
when travelling with the airline. BA's brand promise
is a combination of both emotional and functional
benefi ts, which manifest themselves through the
company's customer service operations. In addition
to its main brand, BA also has sub-brands that are
targeted at particular segments of the market.
These sub-brands include First, Club World, World
Traveller Plus and World Traveller.
Weblink
Check out this website for full details of
BA's business activities.
www.ba.com
Launch
Growth
Saturation
Decline
Maturity
TIME
USPs
Fig 5.4 - The product life cycle in
travel and tourism
Travel and tourism is a very competitive sector and
organisations work hard to make their products and
services more appealing to potential customers.
Some companies try to develop a USP (unique selling
proposition), which is a special benefi t that one product
or service has over another, e.g. the USP of a car hire fi rm
may be that it rents Ferrari and Porsche cars for special
occasions. A company's USP may be truly unique, for
example a trip on the Venice-Simplon Orient Express
or a ride on the London Eye, but is more likely to be
a product feature that the organisation promotes to
attract attention from customers, for example an airline
that has the most legroom in business class of any of its
competitors may use this as its USP.
Figure 5.4 shows us that the fi ve stages in the product
life cycle are:
1.
Launch - the product is launched with a lot of
money spent on promotion, which hopefully results
in encouraging sales;
2.
Growth - sales grow steadily and profi ts increase.
Competitors may enter the market;
3.
Maturity - sales begin to slow down, perhaps
because competitors are offering a product with
greater benefi ts or at a cheaper price. It is often at
this point that the organisation will need to decide
to either let the product die, re-model it or increase
marketing support to generate more sales;
Product life cycle
All products, whether they are in the travel and
tourism sector or the consumer goods market, have
an identifi able lifespan. There will come a time when
the product is no longer in demand at all, or needs
remodelling in some way to keep its customers.
4.
Saturation - sales have reached a plateau;
5.
Decline - sales drop off quickly and profi ts fall.