Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
-
Ω
=
×
i∈AG
Ω
i
is a finite set of observations, where
o
i
denotes the set of
observations agent
i
can make.
-
O
is a table of observation probabilities.
O
(
s,
a
,s
,
o
)
is the probability of
o
o
1
,...o
n
a
observing joint-observation
in
state
s
and transitioning to state
s
. Each agent
i
only perceives element
o
i
from the joint-observation
=
when executing joint action
o
.
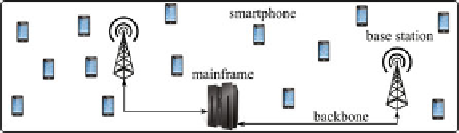
Figure 3 illustrates the considered partitioning problem, which basically is a
cooperative game. In this application, a set of mobile devices should distribute
equally onto a set of base stations. This has to be accomplished in a decentral-
ized manner and it is assumed that mobile devices can only communicate with
base stations within their communication range. The system state is described
by a list of tuples
, that defines for each mobile device
d
i
a currently
selected base station
b
j
. States are evaluated according to optimization criteria,
which are i) to assign the same number of agents to each base station and ii)
to minimize the sum over all radio distances between a mobile device and its
selected base station. The actual assignment quality is calculated by a central
computer that is connected to all base stations via a backbone network. Since,
from a multiagent perspective mobile devices represent agents of the system, we
will use the two terms interchangeably. Formal details on this multi-objective
optimization problem can be found in [12].
Based on the description, the conversion to a Dec-POMDP is straightforward:
d
i
,b
j
-
the state set
contains all assignments of mobile devices to base stations; a
start state
s
0
can be chosen arbitrarily from
S
.
-
a mobile device has one distinct selection action for each base station.
-
the state transition function is deterministic, as a joint action immediately
leads to a new state defined by the joint action.
-
the reward equals the solution quality.
-
devices only observe elements located within the communication radius.
-
the table of observation probabilities
O
is constructed such that with high
probability agents observe the correct system state.
S
The mainframe, as central instance of the environment, is able to calculate a
reward which can be submitted to agents via the base stations. Note that the
Dec-POMDP has no assumptions on the reward function. Accordingly, because
the mainframe knows the current assignment of agents to base stations, it could
Fig. 3.
Partitioning problem: mobile devices such as smartphones should distribute
equally to a set of base stations while minimizing the sum of communication distances