Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
liposomes, nanolipidsomes, lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers,
nanoemulsions, polymeric nanoparticles, lipid nanocapsules, lipid-polymer com-
plexes, lipid-polymer nanoparticles, nanocrystals, dendrimers, fullerences, and
nanoshell are widely studied as drug delivery systems by academia and industries.
On the other side, carbon nanotubes, graphene nanoparticles, metal nanoparticles
and quantum dots are emerging nanomaterials used in imaging, diagnosis and as
drug delivery systems. These systems provide efficient organ and cellular targeting.
Functionalization of the surface offers additional manipulation to the behavior of
nanoparticles in vivo. Overall, nanoparticles or nanomedicine is the future of 21st
century.
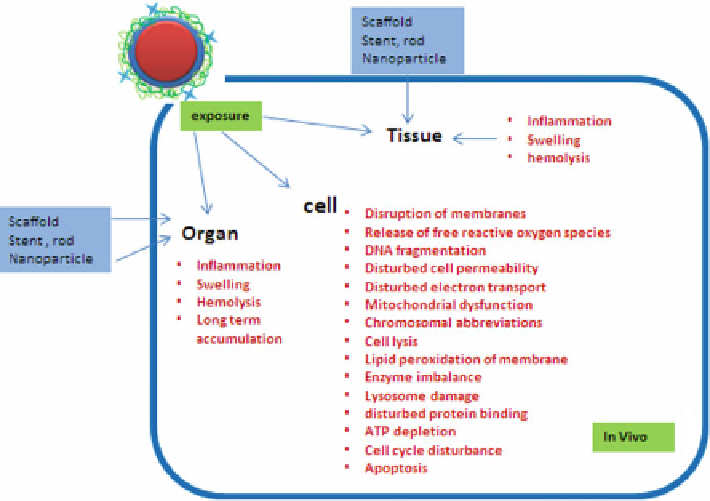
Nanoparticle-induced toxicity involves generation of oxidative stress (free rad-
ical or reactive oxygen species generation, ROS), inflammation, genetic damage,
and the inhibition of cell division and cell death. ROS stress further causes
genotoxicity, inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis by release of some harmful
cytokines (Fig.
6.1
).
Each nanoparticle has unique mechanism of ROS generation which is till date
not fully understood, e.g. metal nanoparticle induce ROS via Fenton-type reactions
while carbon nanotubes by secretion of harmful cytokines. The damage of mito-
chondria and some cellular organelle is induced by nanoparticles without genera-
tion of any ROS. This could also be the case with stents and scaffold implanted.
Fig. 6.1 Interactions of nanoparticles and cellular components and induction of related toxico-
logical effects